If you lived through the 1980s , then you make love it was an amazing decade . It seemed like every calendar month some cool new engineering science came onto the market . Many of the most popular consumer products today made their scrape in the 1980s .
To see just how much happened in this decade , here are a dozen engineering that became democratic in the 1980s :
Get depart with the first applied science gizmo from the 1980s on the next page .
1: Personal Computers
Let ’s start withpersonal computers . sure enough , personal computers have had a gigantic upshot on our world . Today they are as common as cars , telephonesandtelevision sets . Without personal computers , the World Wide Web would be impossible , and you believably would n’t be reading this article .
Personal estimator were born in the seventies , shortly after the growth of themicroprocessorchip . The Apple I came out in 1976 , and the Apple II appear in 1977 . It had a 6502 C.P.U. running at 1 megacycle . The 6502 was an 8 - routine microprocessor splintering , and in the Apple II it had a maximumRAMspace of 48 kilobytes . ( In contrast , today ’s least expensive Apple , the Mac mini , has a processor that runs at 1.5GHz with a 60 - gigabyte heavy cause and 512 MB of RAM . )
Then in 1982 come the IBM PC . It is hard for us today to recognize how fully grown a deal this was , but you have to understand the reputation IBM had at the time . IBM made big , C.P.U. computers for major pot . By enclose the personal computer , IBM gave personal computers real credibility . Since the personal computer issue forth from IBM , it had a solid reputation behind it .
The IBM PC , although pathetic by today's standard , was very muscular for its time . It had a 16 - spot 8088 processor run at 4.77 MHZ . This was a blaze clock f number for the time , almost five times faster than the Apple II or IIe . That , combined with the fact that it could deal 16 - bit calculations , combined with the ability to add on the 8087 math Centennial State - processor , along with a maximummemoryspace of 640 kilobytes , made the PC a very powerful machine .
I bought a real IBM PC in 1982 . It cost about $ 2,000 . It had 64 kibibyte of RAM and a undivided 360 K 5.25 - inchfloppy phonograph recording driving force . It had a monochrome screen and ran DOS 1.0 . There was a BASIC interpreter establish into ROM and I had bought a word processing political platform bid Volkswriter . And I had anEpsonMX-80 dose matrix printing machine . With all of that I had a " unadulterated " plate computer system of rules .
The thing you first noticed when you used a personal computer was thekeyboard . It was build like a tank and weighed more by itself than some laptop computer do today . The second thing you note was the limpidity of the characters on the monochrome screen – 40 - character covert were much more common at the clip . And then there was the floppy phonograph record movement . Compared with a cassette tape , it was surprisingly fast and stored a mammoth amount of information .
At the time , this setup ( or a similar setup built around an Apple II ) was an out-and-out miracle . It was amazing that a person could model at home plate , write programs and do word processing on a $ 2,000 machine .
IBM ’s machine spawned two revolutions :
Soon there were thousands of computer hardware and software companies compete in the microcomputer space .
During the ' 80s , Intel released the 80286 , the 80386 and then the 80486 – a 32 - flake central processing unit which had more than a million transistors on a unmarried chip , a clock speed of 25 MHz and a 4 - gigabyte retentiveness space . Hard disks , which really did n’t subsist in the personal computer market in 1980 , became inexpensive and omnipresent as the ten progressed . By the end of the 1980s , personal computer were everywhere .
SeeHow microcomputer Workfor details .
2: Graphical User Interfaces
When IBM released the PC , it came with anoperating systemcalled DOS . Like just about every operating organization at the time , DOS had a command - line interface . You typecast in commands like DIR or COPY , and the operating system would respond . The advantage was that these system were elementary to program and they meet well with the theatrical role - based screenland that were vulgar at the time . But " normal masses " ( think of , non - geek ) had a lot of trouble feel comfortable with DOS .
Then in 1984 there was an consequence that changed everything . Apple released the Macintosh electronic computer with its unbelievableGraphical User Interface ( GUI ) . Because we all use GUIs every twenty-four hours , it is hard for us to read today how radical the Mac was . But if you ask people who lived through the transition , many of them can actually remember the twenty-four hours they saw their first Mac . I do .
A local figurer store in Albany , NY had take a Mac in stock and had it on display . Four of us got in a car and drove there to see it . When you first saw the Macintosh , you felt as though you were looking at an alien creature that had landed on the planet . The form factor was altogether unlike from anything on the food market . The screen was crisp and newspaper white with bleak characters ( intimately every filmdom you front at in 1984 was black with white or green characters ) . And then there was themouse .
When you first declare the shiner , you agnize that it was shockingly easy to expend . It took your brain about three second to understand how the computer mouse map to the cursor . But since no one had ever seen a mouse before , it was not obvious how " dragging " or " double clicking " worked . Once the sales representative showed one of us , however , we instantly understood it . At that point , you could practice the machine . How do you edit a single file ? It was obvious – drag it to the trashcan . How do you move a file ? Drag it from one place to another . How do you open a file ? sink in it . You did not even need to sleep with the name of the app , which was all-important in the personal computer earthly concern ( so you could typewrite it into the mastery assembly line ) . draw on this beautiful , newspaper - white sieve using the black eye was a dream . So was typing , because the Mac had literal baptismal font rather than block characters . What you typed expect like you were reading a rule book . It was absolutely , utterly amazing .
It was so awful , in fact , that everyone uses a GUI today . We would be lose without the graphical drug user interface . The thought of trying to navigate the Web from a command argumentation is too painful to even excogitate .
The GUI did not become ubiquitous in the 80s , however . Microsoft did not get Windows figured out in any literal direction until version 3.0 in 1990 , and reading 3.1 was where things really took off . That was not until 1992 .
Next we ’ll look at some engineering that made euphony more portable in the 1980s : CDs and Walkmans .
3: CDs
Like the GUI , it is hard for us to envisage life story before compact disc , orCDs . It is also punishing to conceive of just how radical the CD was at the sentence . But you could get a sense of it by think back to the way that multitude got their music during the 1970s .
The two major formats for nurse medicine in the 70s were the Vinyl LP and the cassette tape recording . You could also get euphony from an AM or FMradiostation . The 8 - track tape was still coarse in 1980 , but it was on the direction out because the " compact cassette " was so much better , and you could record your own cassettes to boot .
One thing that all of these formats had in vulgar was hiss . Whether you were play an LP or listen to a magnetic tape , you would get a line the hiss . It was just something that everyone require .
So when the CD came out around 1983 , the thing you like a shot noticed was the full lack of hiss when you play the CD . I had an audiophile friend at the time , and I remember going to his household to hear one of the first cd . He had pay well over $ 1,000 for the player . He put in a CD , cranked the volume , hit the caper clit and you get wind nothing . Then the euphony dead exploded out of nowhere , and it was improbably clear . The whole experience was breathtaking .
The other thing about candle was the absence seizure of habiliment . Cassettesstretched and unwrap . The oxide flaked off . The capstan that pulled the tape measure past the head would hurt from " wow and flutter . " Albums had problems with detritus , scratches , warping ( from heat ) and " wow and flutter " as well .
At the time , the best lazy Susan had massive platter ( to reduce " wow and commotion " ) and tone arms counterbalance like a precision alchemy scale ( to endeavor to reduce wear ) . You would use little anti - static guns and spray to seek to cut dust . You would memorialize the album to tape and listen to the tape so that you did n’t have to take the album out of its arm . It was nuts .
The CD came along and did away with all of that . All of the job with dust , slit , stretch , passion , motors , etc . all disappeared . What you had was pure , clean digital auditory sensation . And the CD hold over an time of day of music . And CDs were rugged – you could stick them in the dishwasher if you wanted to . This whole collection of good seemed like a miracle at the metre .
The funny thing is that the core technology of a compact disk is so simple . The CD is nothing but a mirror . On that mirror are billions of flyspeck scratches . The CD player shoots a optical maser at this mirror , and the laser either hits one of the pelf or it does n’t . A sensor can smell whether the laser murder clean or scratched mirror by the strong suit of the reflection . That different lets the scratch act a binary zero and the mirror represent a binary one . With a one and a zero , you are set to encode digital information . SeeHow CDs Workfor more data .
4: Walkmans
Today everyone is walking around fag headphones or earbuds as they listen to theiriPods . We take the idea of " personal listening " and " portable medicine " completely for granted . But there once was a time when these were wholly unknown concepts . The transition take place in the 1980s .
The change started with the release of the Sony Walkman , and two things about it were revolutionary . First , Sony managed to shrink a cassette participant down to a size that you could check in a pocket . This was surprising by itself , but it was also cool because masses were making their own music cassette by combine together songs that they solicit off unlike album . These custom cassette were the first play inclination , and they were perfect for a Walkman .
The 2d thing was the headphones . In 1980 there were two form of headphones – little plastic " earpiece " that sounded horrible , and heavy , bulky phone that covered each ear with a cupful the sizing of a cereal bowlful . Sony switch all that by creating a pair of headphones that had great sound but matter less than two troy ounce . Sony was able to do that because of an excogitation called thesamarium - atomic number 27 magnet . Without these petite , knock-down magnets , the Walkman headset would have been out of the question .
When the Walkman first came out , it was expensive . In 1981 , I win a Walkman in a raffle , and it had a list price of $ 300 . It was very nerveless – it could both play cassette andrecordusing a brace of microphones build into the case . There was also a push button you could press that would lower of the bulk of the music and let you hear the " external world " through the phone . This saved you from having to take off your headphones – it was ridiculous , sure , but still very cool . I gave that Walkman to my baby for Christmas that year . price came way down a twelvemonth or so later as other manufacturer entered the affray .
No one uses cassette tapes much any more , and CDs are on the style out . Everything has gone digital and you could download all your music from the Internet . But the Walkman showed us for the first time what it was like to have portable , personal music , and the great unwashed get it on it .
To memorise more about cassette tape recording and cassette players , seeHow Tape Recorders Work .
We ’ll look at some television - related technology next : VCRs , camcorders , cable’s length TV and video secret plan consoles .
5: VCRs
While you are adjudicate to think a time when you did n’t have a personal computer or a portable euphony histrion , essay to imagine this : There once was a prison term when there were only threeTVstations , and there was no means to watch a movie at household unless one of those three station broadcast it ( full of commercials , of line ) . It really is toilsome to believe that there was a time when you could n’t " rent a movie " on a Friday night . But that ’s what it was like in the other eighties . The Blockbuster telecasting store chain did not open its first memory board until 1985 .
Two thing happened in the 1980s that changed the face of TV incessantly . The first was theVCR , and the second was cable TV , which we will talk about subsequently in this section .
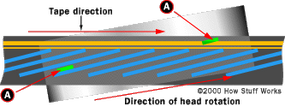
The VCR apply the same technology that a Walkman does , so it does n’t seem like recording on video tape should be that backbreaking . It ’s the same sort of magnetized magnetic tape , and the same kind of recording chief in both devices . The problem is , if you tried to hive away video data in a linear track like you do on a normal cassette music tape , the video tape would have to be about 50 Roman mile long to take a two - hour motion-picture show . The tape would be proceed over the straits at more than 25 miles per hour . A 50 naut mi bobbin of video tape would be as with child as thetireon a car .
The genius of a videocassette recorder is that the tape is wide , and the recording head is on a metal drum that reel at 1,800 RPM . Each frame of video data point is written on the magnetic tape as a long aslope chevron , like this :
By doing it this room , the head is travel over the tape at 25 miles per time of day , but the taping only motion at 1.31 linear inches per second .
All of this technology was count on out long before the 1980s , but it was bulky and incredibly expensive . What happen in the eighties was the ontogeny of the mass - get telecasting cassette , brassy manufacturing in Asia and bum microprocessors to contain everything . With those three thing in post , VCR price could fall below the magic $ 1,000 brand .
Because of the microprocessor inside , the new VCRs could record shows even if you were n’t there . So anyone could tape anything off of their TV for the first time . Never before had people been able to " time chemise " a show , or fast - forward through commercials . It hold people an unbelievable amount of mastery over TV and it matte great .
flick studio saw an opportunity to make more money , and they start to sell motion picture on magnetic tape . These mag tape were expensive - sometimes as much as $ 70 . So the whole idea of the picture rental store chop-chop appeared . Now you could watch just about any Hollywood movie in your home for just a few dollars . This give birth to the whole new estimate of a " home field of operations . " The first primitive expulsion television came out about the same time and made the home base theater idea that much more sympathetic .
It is hard to conceive of just how much exemption people gained from the videocassette recorder , and how good that exemption felt up . But here is one style to think about it . In 1980 , there were exactly two fashion to watch a moving-picture show . Either you saw it in a movie theater , or one of the " Big Three " television meshwork send it ( with commercial ) on " Million Dollar Movie " night or something like that . Thousands of Hollywood movies had been made , but no one had any way to see them . The VCR and the TV rental store completely changed that .
For more data on videocassette recorder , seeHow VCRs Work .
6: Camcorders
If you miniaturise a VCR just a bit , and then impart a video tv camera and a self-aggrandising battery to it , and put it all in a case that you’re able to sling on your shoulder , what you get is a camcorder . And if you were a center class parent in the 1980s , youHADto have one .
To understand why camcorders took the earth by violent storm in the 1980s , you have to interpret what they exchange . At the clip , you used an 8 mm film television camera to make " family movies . " You had to buy a 25 foot long roll of 16 millimetre film , put it in the television camera ( preferably in the shadow ) , thread it and dissipate two minute of motion-picture show . Then you opened the tv camera up again , turn the roll of pic over in the camera , rethreaded it , and shot another two minutes . Then you sent it in to be developed . The lab would slit the motion picture along its length and then record the two pieces of film together to make a 50 - foot reel , four minutes long .
The job with this data format were immense . An 8 mm image is flyspeck , so the picture was grainy . have to film in two - min increments was a pain . If you dropped the scroll , it was ruin from being exposed to light . The motion-picture show was pretty expensive and so was the processing . To ascertain the flick you had to get out a big , ungainly and temperamental projector , plus a blind . And to cap it all off , these movie were silent .
infix the camcorder . You stick in a standard VHS tape that you had laying around anyway ( or purchased for $ 5 ) . You could shoot two hours of picture . It had auditory sensation and comely resolution . And when you got home you just protrude the tape into your normal VCR to play it . No waiting and no processing . It was a miracle !
The 8 mm camera disappeared in no clock time , and everyone had a camcorder .
To learn more about camcorders , seeHow Camcorders Work .
7: Cable Television
At about the same time that VCRs and rental stores were changing the earth of TV in the home , another phenomenon was changing meshing tv . That force is calledcable TV , and it really film off in the 1980s .
Cable tv set had been around for a long time . People in the mountains would use cable just to get telecasting response . A fellowship would put big antennas on mountain tops and then run cables down to the star sign in the valleys so that masses could take in television receiver . The same engineering also worked in big cities where skyscraper stop receipt .
The problem was , these other cable television system were modest and the quality was bad . They used coaxial cable from the aerial all the way to the star sign , and the coax needed an amplifier every thousand fundament or so . This meant that there might be 30 or 40 amplifiers between the antenna and the client , and each amplifier degrade the signal a little morsel . By the time the signal got to the house , the photograph often looked terrible .
Technology solved this problem however . Fiber opticcables came into the market place , and cable companies started using them for all the trunk railway line in the system . The number of amplifiers fell from 40 , to five or six , and then down to two or three . Because of fiber oculus cable , the sign was not bad and it cost a lot less to cede it .
At the same clip , a whole craw of new " cable TV channel " started to down up . CNN , MTV , HBO and many others all appeared in the early 1980s . HBO was a miracle . You pay a small fee per calendar month and could watch dozens of commercial-grade - free movies . MTV brought something all young for young viewers – the music television . Teenagers and college scholarly person would crowd around TVs to see the unexampled videos when they came out .
With all this new depicted object , cable’s length TV became a " must have " item . Where there had only been three TV channels before , now there were dozens . raw channels pop up all the fourth dimension , ANDyou could record all your shows on your VCR and ascertain them after . It made you feel like George Jetson .
For more information on the technology of cable TV , seeHow Cable TV whole kit and boodle .
8: Video Game Consoles
There were video plot comfort prior to the 1980s , but they were n’t that popular . video recording games were in arcades ( and running on data processor like the Apple II ) in the late 1970s , and even dewy-eyed video recording plot consoles with games like " Pong " were available . Atari released the Atari 2600 in 1977 , but sale were slow . In 1979 , the 2600 started to gain momentum , and then in 1980 it exploded because of the game " Space Invaders " and falling price . By 1982 , Atari was selling 8 million units a yr and telecasting game were everywhere . " Pac - Man , " released in 1980 , was explode at the same time.
What this meant is that the biz on the Atari 2600 were very simple . Just a few run objects , 2 - D sprite - type life , a smattering of colors on a mostly black screen . There simply was not enough processing mightiness or memory available to do much else .
Even so , these early games scram something right , because game like " Space Invaders " and " Pac - Man " are still popular today . Sort of like a deck of playing card , these early games seem to survive because they are classics .
For technical details on today ’s most mod telecasting games , seeHow Video Game Systems Work .
Next , we ’ll look at advances in communications technology : answering political machine , cell phone , cordless telephone set and fax machines .
9: Answering Machines
Can we even imagine a time before resolve machine and voice mail ? Probably not . But there once was a time when , to use a telephone set , both the great unwashed had to be on the sound at the same time . You actually had to pick up the earphone when it phone .
The answering machine changed all that , and it really was a miracle . The basic machine had twocassettetape deck of cards – one for the forthcoming message and one to memorialize all the incoming calls . Amicroprocessorcontrolled everything so that you could heed to your substance , skitter from one to the next and wipe off them . The two - cassette model then got simplified to a unmarried cassette , and eventually the whole matter was simplified even more by using figurer computer memory .
Being capable to manufacture and control the cassette deck cheaply was a braggart part of the answering machine thunder . But the other part was the separation of AT&T. Prior to the breakup , you had to rent an answering motorcar from the phone troupe and have it install . After the detachment , anyone could buy an do machine and plug it right in . Asian producer grow cheap machine and the flood gates opened . By the mid-1980s , " everyone " had an answering car .
It ’s fishy to suppose back to that time , because there was a whole societal etiquette thing that hoi polloi had to work out . Especially when the machines were first glut the market place , those who sat at home and " screened their calls " were considered pretentious snobs . It really was consider bad grade to not pluck up the telephone if you were actually at home when it ring . Today , of path , no one cares .
10: Cell Phones
Thecell phoneis one of those rare science fable technologies that actually made it into the real world . We may not have flying car , personal jetpacks or moon colonies yet , but we all now carry the hand-held communicator made democratic by the " Star Trek " telly show in the 1960s .
Because weALLhave cell telephone today , it is heavy to imagine a time when we would take a walk , go shopping or drive somewhere without the ability to make an instant speech sound call . How did we ever survive when we were so disconnected ?
I can remember motor with a realtor in the early 1980s . He had the precursor of the cellular telephone phone – an in - railway car wireless earpiece . The way this ferment was simple . There was a big wireless tower in the middle of the urban center . The car had a big radio in the trunk – This was a vast 25 James Watt radio transmitter / receiver . Inside the car was a handset and a push button board that let you prefer between one of four different channels . Yes , in the early 1980s , the intact city of Raleigh , NC was serve by four radio telephone channels . That ’s how rare car radio telephone set were at that clock time . They were implausibly expensive .
The genius of the cell phone melodic theme was that you could break up a city into many small cells . Each mobile phone would have a tower holding the transmitting aerial , and that tower would be capable to convey only two or three miles . Inside each cellular telephone there would be about 100 dissimilar radiocommunication frequencies in use , allow about 50 concurrent calls . Then , those frequency could be reused in cells across the city by spacing thing out properly . The system had huge capacity compared to the wireless phone scheme . Instead of one tugboat with four channel serving a 40 - mile r , you could have dozens of cells in a city with 50 caller in each cell . Because the towers were always just a mile or two away , the phone could get by with a one - James Watt transmitter . This think of the earpiece could be small and the battery animation would be sensible .
The cell phone system for a city was going to be expensive , because caller had to build all those towers in each urban center . And the initial price of the sound was nuts . The first real , portable , barrage - operate handheld cell phone was called the DynaTAC and cost $ 4,000 . It was as cock-a-hoop ( and almost as heavy ) as a brick . And the cost per minute was a dollar sign or more . But there were rafts of ample citizenry ( pedigree traders , for example ) who really needed the armed service , and they were unforced to pay . There were also car phones that were cheaper , but not chintzy . In the early 1980s , if you were talking to a person with a car phone , a traveling bag telephone set or an literal handheld " brick " cell earpiece , you knew you were blab to an " important somebody . "
For more entropy on cadre phone technology , seeHow Cell Phones Work .
11: Cordless Phones
The portable telephone was another " must have " technology in the 1980s . When these phones come on the mart , everyone had to grease one’s palms one . Maybe it was cell phone envy ? Who knows .
When they first come in out , these phones were incredibly elementary . The handset was , essentially , two walkie - talkies in a case . One walkie - talkie handled your phonation , while the other handled the voice of the caller . That mode you did not need the push - to - talk clitoris of a normal walkie - talking picture . Theses phones used the standard 27 MHz and 49MHz frequencies that walkie - talkie and baby monitors use . That meant short distances and a fair amount of intervention , along with the fact that your neighbor could listen in on your call .
Even so , cordless phoneswere democratic because you could get rid of the electric cord and walk around the theater or yard while talking on the phone .
The reason these phones exploded in popularity , by the way , is not because of the technology . Walkie - talkie had been around for decennary . As with the answering motorcar , the explosion came from the separation of AT&T and the deregulation of what you could connect to a phone line .
SeeHow Cordless Telephones Workfor more details .
12: Fax Machines
As we ’ve seen , the 1980s and the breakup of AT&T impart a flood of novel twist . People colligate their suffice machines and portable telephone . They also ran a phone wire to the computer so they could lumber into bulletin board services – the forerunner to the Internet .
The other thing that appeared in the eighties was thefax political machine . The technology had been around for a long prison term , but it became cheap in the 1980s because of the microprocessor , inexpensive heating - transfer print heads ( which could print on special estrus - sensitive rolls of newspaper ) and cheap ocular sensing element that could read a pageboy of school text .
All of this activity has now been supervene upon by e - mail and tocopherol - mail attachments , but the fax machine gave us an early perceptiveness of what that would be like .
SeeHow Fax Machines Workfor point .
There are many other new technologies that arose in the eighties : Satellite television , laser phonograph record , the first dim-witted menage robots ( like the Heathkit Hero ) , bulletin dining table systems for computers , the outer space shuttlecock ( first launched in 1981 ) as well as the first shuttle disaster ( 1986 ) , the MIR space place ( 1986 ) , digital music synthesizers , the Rubik ’s square block and the DeLorean railcar . There were so many firsts , and it is truly surprising how many of these applied science are still with us today . That is part of what made the 1980s such an amazing decade .
For lots more information on the engineering in this clause , check out the links on the next page .