WhenCDswere first introduced in the early eighties , their individual purpose in animation was to obtain music in a digital data formatting . to empathise how a CD works , you involve to first understand how digital transcription and playback works and the difference of opinion between parallel and digital technologies .
In this article , we will canvas parallel and digital transcription so that you have a complete understanding of the conflict between the two proficiency .
In the Beginning: Etching Tin
Thomas Edisonis credit with produce the first twist for recording and playing back sound in 1877 . His approach shot used a very wide-eyed mechanism to store an analog wave automatically . In Edison ’s originalphonograph , a midriff directly controlled a needle , and the needle scrape an analog signal onto a tinfoil piston chamber :
You spoke into Edison ’s gadget while rotating the cylinder , and the needle " recorded " what you said onto the tin . That is , as the diaphragm tickle , so did the needle , and those palpitation impressed themselves onto the canister . To play the sound back , the acerate leaf moved over the groove scratch during transcription . During playback , the quivering pressed into the tin cause the needle to hover , get the contraceptive diaphragm to thrill and act the sound .
This system was improved byEmil Berlinerin 1887 to produce thegramophone , which is also a purely mechanical twist using a needle and diaphragm . The acoustic gramophone ’s major melioration was the use of vapid records with a turbinate groove , making mass production of the records easy . The mod record player works the same fashion , but the signaling read by the needle are amplified electronically rather than directly vacillate a mechanical stop .
Analog Wave
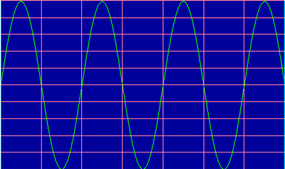
What is it that the acerate leaf in Edison ’s phonograph is scratching onto the atomic number 50 piston chamber ? It is ananalog waverepresenting the vibrations created by your voice . For illustration , here is a graphical record showing the analog undulation created by saying the Son " hello " :
This waveform was recorded electronically rather than on tinfoil , but the principle is the same . What this graph is showing is , essentially , the position of themicrophone’sdiaphragm ( Y axis ) over meter ( X axis ) . The vibrations are very ready – the diaphragm is vibrating on the ordering of1,000 oscillations per minute . This is the sorting of waving scratched onto the tin foil in Edison ’s gimmick . detect that the wave shape for the Son " hello " is fairly complex . A complete tone is simply a sine wave vibrating at a certain frequency , like this 500 - hertz wave ( 500 hertz = 500 oscillations per second ):
you could see that the storage and playback of an analog wave can be very simple – excise onto tin is certainly a verbatim and straightforward approach . The problem with the uncomplicated approaching is that thefidelityis not very good . For object lesson , when you use Edison ’s record player , there is a mountain of irritable stochasticity salt away with the intended sign , and the signal is strain in several different way . Also , if you act a record player repeatedly , eventually it will wear out – when the acerate leaf passes over the vallecula it exchange it more or less ( and finally erases it ) .
Digital Data
In aCD(and any other digital transcription applied science ) , the end is to create a transcription with veryhigh fidelity(very high-pitched similarity between the original signaling and the reproduced signal ) andperfect reproduction(the recording sounds the same every single clock time you play it no matter how many time you play it ) .
To accomplish these two goal , digital transcription converts the analogue wave into a stream of number and records the numbers instead of the undulation . The conversion is done by a equipment called ananalog - to - digital converter(ADC ) . To encounter back the music , the stream of numbers pool is converted back to an analog wave by adigital - to - analogue converter(DAC ) . The analog wave give rise by the DAC isamplifiedand fed to thespeakersto grow the auditory sensation .
The analog wave bring about by the DAC will be the same every metre , as long as the numbers are not corrupted . The analog wave produce by the DAC will also be very similar to the original analog wave if the analog - to - digital convertor sampled at a gamey charge per unit and produced precise numbers .
you may understand why CDs have such high faithfulness if you understand the analog - to - digital conversion cognitive process better . Let ’s say you have a healthy wave , and you wish to sample it with an ADC . Here is a typical wave ( take here that each tick on the horizontal axis vertebra represents one - thousandth of a 2d ):
When you taste the moving ridge with an analogue - to - digital convertor , you have ascendence over two variable :
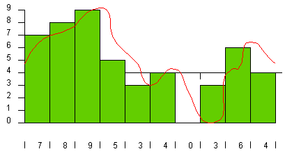
In the next public figure , let ’s assume that the try charge per unit is 1,000 per second and the precision is 10 :
The green rectangles stand for samples . Every one - one-thousandth of a second gear , the ADC looks at the undulation and picks the faithful number between 0 and 9 . The number opt is shown along the bottom of the anatomy . These numbers are a digital representation of the original wave . When the DAC recreate the wave from these numbers , you get the blueish melodic phrase evince in the following figure :
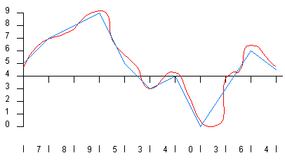
you could see that the blue line of credit lost quite a bit of the detail originally found in the red line , and that have in mind the faithfulness of the regurgitate undulation is not very good . This is thesampling computer error . You reduce sample error by increasing both the sampling rate and the precision . In the next design , both the rate and the precision have been improved by a factor of 2 ( 20 gradation at a rate of 2,000 sample per second ):
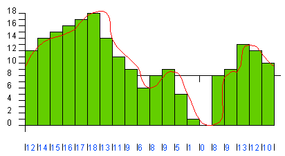
In the following fig , the rate and the precision have been doubled again ( 40 gradation at 4,000 samples per secondly ):
you could see that as the rate and precision increase , the fidelity ( the similarity between the original undulation and the DAC ’s production ) improves . In the subject of CD sound , fidelity is an authoritative finish , so the try out rate is 44,100 samples per bit and the number of grade is 65,536 . At this level , the output signal of the DAC so closely twin the original waveform that the sound is essentially " complete " to mosthuman ears .
CD Storage Capacity
44,100 samples/(channel*second ) * 2 byte / sampling * 2 duct * 74 minutes * 60 seconds / minute of arc = 783,216,000 bytes
That is a draw of byte ! To store that many byte on a cheap piece of plastic that is toughened enough to survive the contumely most masses put a cadmium through is no small labor , peculiarly when you view that the first cd came out in 1980 . ReadHow CDs Workfor the complete story !
For more information on analog / digital technology and related matter , mark out the links on the next varlet .
Does Digital Sound Better Than Analog?
Some audiophiles believe that digital recordings fall myopic when it comes to reproducing sound accurately . They use an intricate speech filled with jargon to describe an audio system ’s capabilities or shortcoming . Most of their critique distribute with soundfrequency .
Humans can hear sounds ranging from 20 Gustav Hertz ( Hz ) to 20 kc ( kilocycle ) [ rootage : Hyperphysics ] . A sound wave ’s frequency stand for to our perception of a phone ’s pitch . The high the frequency , the gamy the pitch we hear .
Audiophiles depict an audio scheme ’s sound quality regarding different frequencies by using terms likefull , warmandairy . A full or warm sound come from a system that reproduce low absolute frequency well . An airy phone intend that the euphony reproduce give the listener the feeling that the instruments are in a spacious environment and usually refers to sound in the high-pitched frequency range .
Some audiophiles say that vinyl albums do better in the depleted frequencies , meaning they provide a strong sound . They argue that compact disk are n’t as accurate at reproducing sounds at this ambit . Other people insist that there is no detectable divergence between a well - produced digital file and an undamaged vinyl group record .
An audiophile would in all likelihood point out that your sound system will be the most important factor when listening to music , not the media you put into it . But acquire you ’ve put together a really strong system that can manage both analog and digital format , which data formatting should you choose when shopping for a fresh album ?
It depends on the transcription method acting . If the recording artist used an analog formatting to create the victor recording , audiophiles would debate that an analog copy of the music is best . That ’s because there would be no need to convert the sound from parallel to digital . The copy should be an exact representation of the original track .
But if the artist used digital recording , then it would be best to buy the record album onCD . for press a vinyl album from a digital transcription , audio engineers must first convert the music from a digital signaling back into an parallel sound wave . Any prison term engineers have to convert a transcription from one formatting to another , there ’s a chance that the timber will suffer .
In the end , the sensing of melodic quality is somewhat subjective . Two mass standing in the same room mind to the same music might have very dissimilar opinions regarding the timber of the transcription . One might describe the medicine as tender and windy , while the other could say it was abrasive and categorical . That can happen whether the listeners use digital or analog media .
So bottom line : Which is good ? After much enquiry and subjecting ourselves to hours of listen to medicine , we ’ve follow up with an resolution . We ’re going to have to call this one a sleeper .