In 1997 , a new engineering come out that brought digital auditory sensation and video into homes all over the world . It was calledDVD , and it revolutionized the film manufacture .
The industry is set for yet another revolution with the introduction ofBlu - light beam Discs(BD ) in 2006 . With their high storage capacity , Blu - ray discs can carry and make for back large quantity ofhigh - definition video and audio , as well as pic , data point and other digital content .
In this article , HowStuffWorks explains how the Blu - re disc full treatment and how it was developed , and we ’ll see how it stacks up against some other new digital video formats on the horizon .
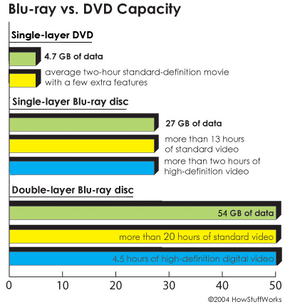
A current , undivided - sided , received DVD can hold4.7 GB(gigabytes ) of information . That ’s about the sizing of an average two - 60 minutes , received - definition motion picture with a few excess lineament . But ahigh - definition movie , which has a much clearer image ( seeHow Digital Television Works ) , takes up aboutfive times more bandwidthand therefore expect a phonograph recording with about five times more storage . As TV sets and pic studio make the move to high definition , consumers are going to involve playback systems with a lotmore storage capacitance .
Blu - ray is the next - coevals digital TV disc . It can record , store and play back high - definition television and digital audio frequency , as well as computer information . The reward to Blu - irradiation is the out-and-out amount of info it can check :
Source : White Paper : Blu - ray Disc Format
We ’ll learn more about the difference of opinion between Blu - ray discs and DVDs in the next incision .
Building a Blu-ray Disc
Blu - ray discs not only have more storage capacity than traditional DVDs , but they also offer a new level ofinteractivity . Users will be able toconnect to the Internetand instantly download subtitle and other interactive picture feature of speech . With Blu - ray , you could :
Discs store digitally encoded video and audio information inpits– spiral groove that run from the heart of the disc to its edges . Alaserreads the other side of these pits – thebumps– to play the motion-picture show or program that is stash away on the DVD . The more data that is contained on a disc , the littler and more closely jam-packed the pits must be . The little the pits ( and therefore the bumps ) , the more exact the reading laser must be .
Unlike current DVDs , which use ared laserto read and write data , Blu - ray uses ablue laser(which is where the format get its name ) . A down in the mouth optical maser has ashorter wavelength(405 nm ) than a red laser ( 650 nm ) . The smaller electron beam focus more precisely , enable it to read information recorded in pits that are only0.15 microns(µm ) ( 1 micrometer = 10 - 6meters ) long – this is more than double as small as the pits on a DVD . Plus , Blu - ray has reduce thetrack pitchfrom 0.74 microns to0.32 microns . The littler pits , smaller ray and light raceway pitch together enable a single - level Blu - shaft disc to hold more than 25 GB of entropy – about five multiplication the amount of data that can be store on a videodisk .
Each Blu - ray magnetic disc is about the same thickness ( 1.2 mm ) as a DVD . But the two types of discs store datum differently . In a videodisc , the data is sandwiched between two polycarbonate layers , each 0.6 - mm loggerheaded . take a polycarbonate layer on top of the datum can make a job calledbirefringence , in which the substrate layer refract the optical maser brightness level into two separate beams . If the beam is separate too wide , the disk can not be read . Also , if the videodisc surface is not precisely flat , and is therefore not precisely perpendicular to the beam , it can lead to a job known asdisc joust , in which the laser beam is distorted . All of these issues lead to a very involved fabrication process .
Learn how Blu - shaft overcomes these obstruction in the next plane section .
How Blu-ray Reads Data
The Blu - ray disc overcomes videodisk - read issues by placing the dataon top of a 1.1 - mm - duncish polycarbonate layer . Having the data point on top prevents double refraction and therefore prevents readability problem . And , with the transcription layer sittingcloser to the objective lensof the reading chemical mechanism , the problem of magnetic disk tilt is virtually eliminated . Because the information is closer to the aerofoil , a hard covering is placed on the outside of the disc to protect it from scratches and fingermark .
The design of the Blu - ray of light discs bring through on manufacture toll . Traditional videodisc are built by injection molding the two 0.6 - mm discs between which the recording layer is sandwich . The process must be done very cautiously to prevent double refraction .
Blu - ray discs only do the injection - cast cognitive operation on a single 1.1 - millimeter saucer , which reduces cost . That savings equilibrate out the cost of adding the protective layer , so the goal price isno more than the monetary value of a regular DVD .
Blu - shaft of light also has ahigher data transfer rate–36 Mbps(megabits per instant ) – than today ’s DVDs , which transfer at 10 Mbps . A Blu - ray disc can record 25 GB of material in just over an hour and a half .
We ’ll search at some of Blu - ray ’s competition in the next section .
Blu-ray Competitors
Will Blu - ray replace late DVDs ? Its producer hope so . In the meantime , JVChas developed aBlu - ray / DVD combo discwith an approximate 33.5 - GB capacity , set aside for the release of telecasting in both formats on a individual disc . But Blu - ray is not alone in the marketplace . A few other formats are competing for a parcel of the videodisc market .
The other big player isHD - DVD , also calledAOD(Advanced Optical Disc ) , which was developed by electronics giantsToshibaandNEC . HD - DVD was actually in the works before regular DVD , but it did n’t begin veridical development until 2003 .
The reward to HD - DVD is that it uses the same introductory format as the traditional DVD and can therefore bemanufactured with the same equipment , saving on cost . HD - videodisc match the reposition capacity of Blu - re . A rewritable , single - layer HD - DVD can hold 15 GB of information , a double - stratum disc can take hold 30 gibibyte , and a triple - level disc can take for 45 GB ( that ’s compared to 27 GB and 50 GB for Blu - beam ) . The read - only version hold slightly less information . Also , HD - DVD offer the interactive capabilities of Blu - ray , with HDi . For more information on HD - DVD , check outHow HD - DVD Works .
Blu - ray and HD - DVD are the two major competitors in the market , but there are other contenders , as well . Warner Bros. Pictures has develop its own scheme , calledHD - DVD-9 . This organization use ahigher compression rateto put more information ( about two hours of high - definition video recording ) on a standard videodisk . Taiwan has create theForward Versatile Disc(FVD ) , an upgraded version of today ’s DVDs that allow for more data storage capacity ( 5.4 GB on a single - sided disc and 9.8 GB on a dual - sided disc ) . And China has introduce theEnhanced Video Disc(EVD ) , another high - definition picture disk .
There are alsoprofessional versionsof the blue optical maser technology . Sonyhas developedXDCAMandProData(Professional Disc for Data ) . The former is design for economic consumption by broadcasters and Ab studio . The latter is chiefly for commercial datum storage ( for example , backing upservers ) .
It seems that the time to come holds a whole lot more than 25 to 54 GB on a single magnetic disk . grant toT3 : Pioneer goes beyond Blu - Ray , Pioneeris developing an ocular saucer that will blow away the severe disc in most of our PCs in terms computer storage capacitance , holding500 GBof data point . How so ? Pioneer ’s lasers areultraviolet , which have an even shorter wavelength than the blue .
For more selective information on Blu - ray and related topic , check out the nexus on the next page .
Frequently Answered Questions About Blu Ray
Lots More Information
Related HowStuffWorks Articles
More Great Links
Sources