In the early days of bowling , respotting the pins was a physically demanding job . There were actually people behind the lanes readjust the pins and sending back the glob .
Today there are awesome robotic devices that do all the pin setting . Theautomatic pinsetter , first patented by Gottfried Schmidt , was introduced by the American Machine and Foundry Company ( AMF ) in 1946 . This first pinsetter was a monster , weighing nearly 2 rafts ( 1.8 metric wads ) and stand 9 groundwork ( 2.7 m ) tall .
Modern pinsetters are but a fraction of a size of it of their predecessors and much more reasoning . In this article , you will see how bowling pinsetters are able to pick up standing rowlock , reset the lane of any knocked - over pins and accurately readjust the pins after every lump .
Bowling Basics
Many unlike versions of the game subsist around the man , but the most popular istenpin bowling . You roll a bowling musket ball down a slick lane to pink down10 pins , which are in atriangular arrangementfacing you . On either side of the lane areguttersthat will snare the glob if it slue too far to either side of the lane .
A solidifying of 10 pins is known as arack . A plot is made up of10 frames . The business of the pinsetter is to create each rack at the beginning of each frame , and clear away knock - over pins so they do not get in the mode . Most modern bowling facilities havecomputerizedbowling lane that expose your score automatically throughout the game , and the electronics and sensors in the pinsetter also avail keep track of the score .
Now let ’s discover about the machine that set up the pins after every roll .
As the Pins Fall
The pinsetter sit quietly at the end of the bowling lane , waiting for the bowler to roll a ballock toward the pin . ABrunswick GSX pinsetter , which is the one we will look at in this clause , is one of the fresh pinsetters in the bowling industry . The Brunswick pinsetter lie in of four independent persona :
Altogether , there are over4,000 someone partsthat go into resetting the pins after you roll !
An automatic pinsetter figure out with a full of20 pins , twice the number call for for the 10 - tholepin arrangement . The pinsetter goes to oeuvre incycles , lay out procedures that are executed after a orchis has been rolled . To be able to respond appropriately , the pinsetter needs to know just what has come about below it on the lane , whether it be a ten-strike or a gutter chunk . Modern pinsetters interface with a smallCCDscanner camerathat is mounted far down the lane . The camera quickly senses precisely which pins have been knocked down , and then relays this entropy to the pinsetter . In one-time pinsetters , this function was performed by the pinsetter itself . It would lower itself onto the lane and utilize " fingers " to determine which pins were n’t abide . Most newer pinsetters still have the " finger " as a backup to the CCD photographic camera – they may use them during situations when the camera can not function decent .
The next step depend on exactly what has occurred on the lane . permit ’s examine the wheel that most often pass off when amateur bowlers are on the lane , typically called the " first ball - standing pins " cycle . This cycle runs when a bowler , on the first roll , knocks down between one and nine tholepin . The pinsetter needs to execute three distinct task :
The process is pose in motion after the derby hat drift a ballock down the lane .
Now that the stay pins are out of the way , it ’s time to get rid of the pins forget on the lane !
Out with the Old
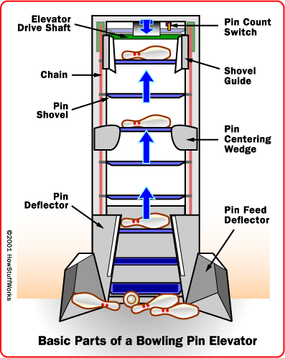
The next stride is to sweep away thedeadwood . The sweep that had been in the " guard " emplacement is pulled back and forth one time in edict to sweep away the knocked - down pins that are still on the lane . These flag are then impress viaconveyor beltback into thepin elevator . They will be be used in the upcoming frame .
The preloading of the next frame ’s pins can only be done in machines in which a CCD camera is used for scoring and pin - count function . Otherwise , the pin table require to lower itself empty after the 2d ball is rolled to provide pin - count entropy to the automatic scoring simple machine .
The comportment ( or deficiency of ) a television camera , along with the result of the second ball , will regulate the next cycle . simulate that a camera is present , the next cycle consists of a simple sweep of the pins and a placement of 10 new pin on the lane for the next form . Several other cycles are potential , however , include preset cycles/second forfoulsandout - of - range pins .
new pinsetters have advanced features and cycles that speed up play . The computer baron in new pinsetters allows them to make more intelligent decision , effectively diminish postponement . One deterrent example of these advances is theshort cycle . Short cps are specific bike that are run if the 7 pin or 10 pin is knock down and if no pins are knock down . In these cases , there ’s no deadwood , so no end run motion is necessary . This save not only time but also wear on the machine .
Let ’s obtain out what else is going on behind the scenes .
Behind the Scenes
Two other office of the pinsetter that are not see by the bowler are theball acceleratorand thepin elevator . The testicle accelerator returns the ball to the bowler at the other end of the lane through a conveyor - like system .
After a roll , the clump and the tap - down pins are located behind the lane in theball cavity . Below the ball pit is a conveyor rap call thetransport ring . The pins and ball flow onto this band and are moved toward the rowlock elevator . The bowling clump takes a detour at some point along the tape transport band , cut off through a specially designed ball threshold . Only the ball is great enough to trigger the sensor necessary to open up the door , so only the glob can go through . The ball is then accelerated through a conveyor arrangement under the lane , back toward the derby hat for the next roster .
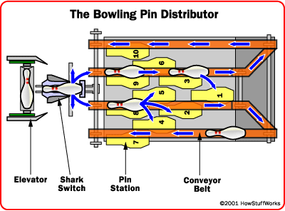
The pins on the transfer band persist in toward the pin elevator . The bowling pin elevator consist of about a dozentrayslocated ontwo pulley block . The pins funnel onto the trays and are raise up toward thepin distributor . The distributor is located above the pin tabular array . It helps place new pin into the pin mesa so they are ready when a new rack is ask .
The allocator has a mechanism know as ashark switchthat pivot a funnel - like tray back and away onto either of two conveyor belts . The position of the switch is determined by electronics in the pinsetter that experience exactly where a novel pin is demand . Each of the two conveyor belt ammunition has a number ofpin stationswhere the stick reconcile into the peg table . The pins are quetch off the conveyor belt into the PIN number place bybumperdevices controlled by the main electronics ( which regulate where a pin tumbler is need ) . Once the raw rowlock are loaded , the pin tabular array pivot horizontally , reverse the bowling pins upright , and lowers them onto the lane at the proper clip .
For mint more information on bowling pinsetters and related topics , check out the links that follow .