From a popular culture stand , theelectric guitaris one of the most important inventions of the 20th century . More thanany other instrument , it set the tone and character of rock and roll music . But when the electric guitar first strike the picture in the 1930s , few people saw its potential . It took quite a while for the instrument to find its shoes in American music .
Despite the irksome scratch , the electric guitar did find its place . It has inhale and defined entirely new types of music . The galvanising guitar stay the most prominent legal instrument in rock ‘n’ roll music , and the most famous instrument ever to come out of the United States .
In this article , you will learn exactly how the guitar itself works , and we will also talk about the system that the guitar and the A create together . Working in combination , the guitar and the amp can produce an amazing mixed bag of sounds .
If you have ever compared an electric guitar to an acoustical guitar , you know that they have several important thing in common . Both acoustic and electric guitar havesix strings , they both tune up those string withtuning pegsand they both havefretson a longneck . Down at the body last is where the major differences are found .
Some galvanic guitars have a hollow or semi - hollow trunk with the resonating tooth decay discover in an acoustic guitar , but the most popular electric guitars havesolid physical structure . The auditory sensation is grow bymagnetic pickupsand controlled by severalknobs . If you pluck a string on an electric guitar that is not plug in , the sound is barely audible . Without a sounding board and a vacuous body , there is nothing to amplify the string ’s vibrations .
In the next section , we ’ll see how the magnetised pickups on an galvanic guitar sentiency vibration and turn it into sound .
Electric Guitar Pickups
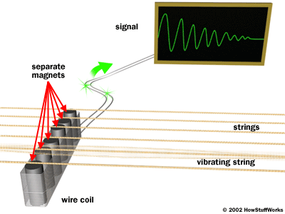
To produce phone , an electric guitar sense the vibe of the stringselectronicallyand gouge an electronic sign to an amplifier andspeaker . The perception occurs in amagnetic pickupmounted under the bowed stringed instrument on the guitar ’s body . A simple magnetised pickup arm looks like this :
This getaway consists of abar magnetwrapped with as many as 7,000 turns of finewire . If you have readHow Electromagnets Work , then you live that coils and attracter can turn electrical energy into apparent movement . In the same way , they can turn motion into electric Energy Department . In the cause of an electric guitar , the vibrating steel string produce a corresponding quivering in the magnet ’s magnetized field and therefore a tickle current in the roll .
There are many different type of pickups . For example , some pickups strain a single magnet cake under all six strings . Others have a disjoined polepiece for each string , like this :
Some pickups use nooky for polepieces so that the height of each polepiece can be adjusted . The closer the polepiece is to the drawing string , the impregnable the signal .
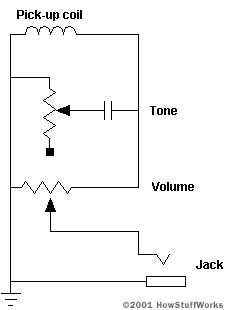
The pick-me-up ’s coil send its signal through a very simplecircuiton most guitars . The circuit looks something like this :
The upper variable resistance adjusts thetone . The resistor ( typically 500 kilo - ohms max ) andcapacitor(0.02 microfarad ) spring a simple dispirited - pass filter . The filter cuts out high frequencies . By adjusting the resistor you control the frequencies that get cut out . The second resistor ( typically 500 kilo - Georg Simon Ohm max ) controls theamplitude(volume ) of the signal that reaches the knave . From the jack , the signaling runs to an amplifier , which drives aspeaker .
Many galvanising guitars have two or three different pickups located at different item on the body . Each pickup will have a distinctive sound , and multiple pickup truck can be match , either in - phase or out , to bring forth additional variations .
Next , we ’ll reckon at the part of the amplifier .
Amps and Distortion
Most electric guitars are completelypassive . That is , they deplete no power , and you do n’t have to plug away them into a big businessman provision . ( Some do have " active " electronics powered by an onboardbattery . ) The vibration of the strings produces a signaling in the pickup whorl . That bare , unamplified signal is what comes out of the guitar and into the amp .
The amp ’s job is to take the guitar ’s signal and make itaudibleby boosting it enough to drive aspeaker . The bewitching thing about an galvanising guitar amp is that the adenosine monophosphate is actually a part of the instrument .
The part of an galvanising guitar amp is completely different from theamplifier in a stereo organization . A stereoscopic photograph ampere is meant to be pellucid – its job is to multiply and amplify sound with as littledistortionas possible . With an galvanizing guitar amp , musician often seek distortion as well as the option of a " fresh " sound . Distortion results when the signal in an amp ’s circuitry is too powerful for that circuitry . The distorted shape is really a part of the desired sound , and many AMP are design so that guitarist can control the tier of overrefinement .
Musicians may also take advantage offeedback loopsbetween the amp and the guitar . If the sound coming out of the amp and speaker is loud enough , it can cause the guitar ’s strings to vibrate . The instrumentalist can hit a note of hand with the guitar , and the amp will do that string to continue vibrating indefinitely . Both of these concepts – amp distortion and feedback – are unequalled to the electric guitar .
you’re able to get a line the effect of distortion in these three examples :
A distinctive amp has at least three parts :
Some adenylic acid also includeeffectsandreverb circuitsbetween the pre - amp and the power amplifier .
The job of thepre - ampis to boost the guitar ’s sign enough so that it can actually ride thepower amplifierstage . Because an electric guitar is inactive , its sign does not have enough power to drive the superpower amp directly .
One of the interesting things about many galvanizing guitar amplifier is the use ofvacuum tube . Vacuum tubeshave distortion patterns and characteristics that are do it and roll in the hay by many instrumentalist . These musicians seek out tube amps with specific tubes and specific amplifier circuit ( for illustration , Class AversusClass ABamplifiers ) to get the exact sound they are looking for .
In the next section , we ’ll reexamine the history of the galvanising guitar .
Electric Guitar History
Engineers begin experimenting with electrically power instrument , such as music box and participant piano , in the 1800s . But the first attempts at an amplified instrument did not come until the growth of electrical amplification by the radio industry in the 1920s .
One of the earliest innovator wasLloyd Loar , an engineer at Gibson Guitar Company . In 1924 , Loar developed anelectric pickupfor the viola and the string basso . In Loar ’s pickup design , the string passed vibrations through thebridgeto the attraction and coil , which register those quivering and passed the electric signal on to an amplifier . The first commercially publicise electrical guitar , made by the Stromberg - Voisinet company in 1928 , use a similar pick-me-up , with vibrations being pick up from thesoundboard .
The goal of these former innovators was to inflate the natural sound of the guitar , but the signal was too weakly . It was only when engineers utilize a more lineal pickup system , in which theelectromagnetregistered chain vibration from the strand themselves , that the modern electric guitar became a reality . The first commercially successful model , the so - called " fry Pan , " was developed and marketed byGeorge BeauchampandAdolph Rickenbackerin 1932 . ( Check outthis sitefor more information . )
The Rickenbacker " Frying genus Pan " was an galvanising Hawaiian model , play flat in the lap , and it caught on now with Hawaiian - style guitarists . The touchstone or " Spanish " style electric guitar , however , fathom so different from an acoustic guitar that it was slow to be accepted . The first artist to develop a playing dash unique to the galvanising guitar was Charlie Christian ( in 1939 ) . At the same time , a few individual begin experimenting with a novel kind of electric guitar , using the same pickup as early designs but mounting the pickup on a solid cube of wood . Les Paul , who was already a well - jazz acoustic guitar player , built such a guitar on a four - by - four piece of pine and nickname it " The Log . “Leo Fender , a former tuner maintenance man , enter a mass - bring out solid - body galvanic guitar in 1950 , and Gibson introduce a model endorse by Les Paul himself in 1952 . The solid - soundbox guitar did n’t have the feedback problem that characterise hollow - body electric guitar , and they had majuscule sustain .
In the 1950s and 1960s , rock’n’roll stars secured Gibson and Paul ’s designs , as well as Fender ’s famousStratocaster , a lasting place in American culture . Since then , every propagation has find a surprising new direction of making the cat’s-paw sing . By all accounts , its potential drop is limitless .
For more information on galvanizing guitar and related topics , check off out the links on the next Thomas Nelson Page .
Electric Guitar FAQ
Lots More Information
Related HowStuffWorks Articles
More Great Links
Please copy / paste the undermentioned text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article :