Most citizenry grew up watching a cathode re tube ( CRT)television . These televisions , while bulky and heavy , had a great picture as long as they got a clear signal . CRT set are still what a lot of people think of when they think of TVs .
But if you ’ve shopped around for a goggle box recently , you ’ve pick up that now there are a lot more options . CRT still crop well for cover sizes up to 40 column inch . But if you want a enceinte concealment , a matted panel TV , widescreen model orHDTVcompatibility , you ’ll have to take from several eccentric of sets , includingliquid crystal display(LCD),digital light processing(DLP ) and smooth crystal over silicon ( LCoS ) .
LCoS is n’t particularly new technology , but it was n’t promptly useable until of late . In this article , we ’ll search at the technology behind LCoS , how it bring home the bacon a exculpated flick and how manufacturers have address number with black tier and contrast .
Review of LCD and DLP
The most vulgar utilisation for LCoS is front- and rearward - projection tv set . The setup is a lot like what you regain in a DLP system . DLP utilise adigital micromirror gadget(DMD ) to create a moving-picture show using a process that ’s like making a mosaic out of small , square tiles . The DMD moderate millions of microscopical mirrors that reflect light from a lamp . Each mirror creates onepixelof the last image .
The mirrors flip-flop back and off between their " on " and " off " spatial relation very rapidly . When mirror are on , they point toward a forcing out lens . The longer a mirror is in the on place , the brilliant the picture element it produce . Mirrors create black pixels stay on off . In most DLP telecasting , acolor wheelspins between the lamp and the DMD , adding red , green and down light to the picture . The viewer ’s eyes combine these colors to create the finished image .
LCoS uses a very standardised idea . As with DMDs , LCoS devices are tiny – most are less than one inch square . Both technology are also reflective – the equipment think over light from a source to a lens or optical prism that collects the light and expose the image . But instead of diminutive mirror that turn on and off , LCoS uses fluid crystals to control the amount of reverberate luminance .
A liquid crystal is a substance that is in mesomorphic province – it ’s not exactly a liquid state or a solid . Its corpuscle normally hold their form , like a solid , but they can also move around , like a liquid state . Nematicliquid crystals , for example , arrange themselves in loose parallel lines . Most LCDs usetwistednematic ( TN ) crystals – with the software of an electric charge , the distorted crystals unbend out .
When placed between twopolarizedpanels , the twisted crystals pass the track of light . By change the direction of the spark , the crystal let or forbid its passage through the 2nd panel . The crystals ' power to alter the course of the light is central to its usage in LCDs and LCoS system .
In their twisted state , liquid vitreous silica organize the brightness so it can pass through the 2d polarized panel .
Ferroelectricliquid crystals ( FLCs ) , sometimes used in LCoS equipment , are crystal which align themselves at a situate slant off from the normal into orderly rows . They also developelectrical polaritywhen they fare into impinging with an electrical charge . Ferroelectric chiral smectic C crystal can switch their orientation very cursorily . you may learn more about smectic and nematic liquid crystals at Kent State University ’s Liquid Crystal Institute .
The liquid crystal layer in an LCoS microdevice see the amount of light for each pixel , like the mirrors do in a DMD . But making the picture requires more than just the microdevice – it also ask lense , mirrors and optical prism .
Projection and Color
It takes several step to create a picture in an LCoS television . The mental process includes a high - intensity level lamp , a series of mirrors and microdevices arranged into a cube , a prism and a projection lense . From first to terminate , here ’s what happens :
Most rear - ejection LCoS televisions use this process . Some projectors use a linear frame-up rather than a cube , and the white illumination strikes surfaces that color it scarlet , green and gloomy before reach the microdevices . A very few systems use only one microdevice along with other methods for supply colour . Some illustration are color wheels like those found in DLP systems or transmissive dyes on the microdevices themselves . Some systems use additional polarizers or filters to further improve picture lineament and contrast .
Without the projection lens of the eye , the picture created in this cognitive process would be too minuscule to see intelligibly . That ’s why LCoS technology falls into the class ofmicrodisplays– displays that are too small to see without some kind of magnification .
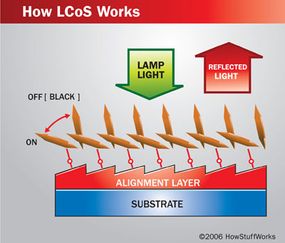
The LCoS Microdevice
or else of using liquid watch glass between two polarize panels like an LCD , an LCoS microdevice has a liquid crystal layer between one transparentthin - film transistor(TFT ) and one siliconsemiconductor . The semiconductor unit has a musing , pixilated surface . The lamp shines visible light through a polarizing filter and onto the gadget , and the liquified crystals act like gates or valves , controlling the amount of light source that reach out the contemplative control surface . The more potential difference a particular pel ’s crystal receives , the more light the watch crystal appropriate to pass . It charter several layers of unlike materials to do this .
From the bottom to the top , here are the components of an LCoS microdevice and what they do :
The exact materials and configurations dissent from producer to manufacturing business . Some utilise nematic liquid crystals and others use ferroelectric crystals . Some employ organic alinement layers , which can infract down through use and exposure to the mellow - vividness light from the lamp . Others use photosensitive material and Inner Light to master the pulse to the fluent crystal .
In universal , LCoS devices have only a very small gap between picture element . Thepixel pitch– the horizontal distance between one pixel and the next pixel of the same color – is between 8 and 20 micron ( 10 - 6 ) . This shrink or extinguish the " projection screen room access " effect found on some DLP televisions and helps keep the image smooth and uniform .
The organisation by and large creates a proficient picture show , but it does have some pro and cons . We ’ll face at those next .
Pros and Cons
The forcible properties of the LCoS microdevice , like the absence of a semblance wheel and the highfill divisor , loosely provide a high - quality picture with a lower limit of artifacts . LCoS pixels are also smooth than the pixels of other systems , which some people say creates more innate delineation . The rainbow and cover doorway effects vulgar to DLP television receiver do n’t exist for LCoS. Unlike LCD systems , they ’re not prostrate to screen burn - in .
However , most LCoS scheme do n’t have a very good dim story , or ability to produce the color black . television with pitiful blackened tier generally ca n’t produce as much contrast or detail as those with good grim point . Since LCoS televisions and projectors use three microdevices instead of one , they also tend to be heavy and bulky . Most require periodic lamp replacement , which can cost several hundred dollar .
In improver , LCoS systems are n’t as common as other video display types . The intellect for this is that LCoS microdevices are difficult to construct , and each set needs three of them . Several company , including Intel , have stress to produce LCoS organisation and have abandoned their cause after systematically small yields in manufacture .
Check out the links that follow for pile more information on liquid crystallization , televisions and related topics .