The computer you are using to record this page apply amicroprocessorto do its work . The microprocessor is the heart of any normal computer , whether it is adesktop automobile , aserveror alaptop . There are many character of microprocessors , but they all do approximately the same thing in around the same way .
A microprocessor — also known as aCPUor cardinal processing whole — is a complete computation railway locomotive that is invent on a individual bit . The first microprocessor was the Intel 4004 , introduce in 1971 . The 4004 was not very powerful — all it could do was add and subtract , and it could only do that 4bitsat a time . But it was awesome that everything was on one chip . Prior to the 4004 , engineers build computers either from collections of chips or from discrete components ( transistorswired one at a meter ) . The 4004 powered one of the first portable electronic reckoner .
If you have ever wonder what the microprocessor in your computer is doing , or if you have ever wondered about the difference between types of microprocessors , then say on . In this article , you will larn how fairly simple digital system of logic techniques grant a computer to do its occupation , whether it ’s play a plot or spell out checking a written document !
Microprocessor Progression: Intel
The first microprocessor to make it into a home computerwas the Intel 8080 , a complete 8 - number computer on one chip , introduced in 1974 . The first microprocessor to make a real splash in the market was the Intel 8088 , bring in in 1979 and incorporate into the IBM PC ( which first appear around 1982 ) . If you are conversant with the personal computer marketplace and its history , you get it on that the PC market make a motion from the 8088 to the 80286 to the 80386 to the 80486 to the Pentium serial to the Core series to the Xeon series . All of these microprocessors are made by Intel and all of them are improvements on the canonic design of the 8088 .
Since 2004 , Intel has usher in microprocessor with multiple cores and millions more transistors . But even these microprocessor succeed the same oecumenical rules as other chips .
An Intel Core i9 CPU can have up to eight cores , each of which can put to death any spell of code that ran on the original 8088 , only about 6,700 times faster ! Each gist can deal multiple threads of book of instructions , appropriate the computer to manage tasks more expeditiously .
Intel ’s product orbit has widen substantially from the seventies . As of this composition , the company still makes Pentium and Core CPUs for computers , but higher - performance PCs and servers may use the Xeon potato chip . In addition , Intel bid the Celeron and Atom mainframe lines . Celeron is train at entry - level computer substance abuser , and Atom processors are better for mobile gadget and devices that are part of the Internet of Things .
While Intel still has a prominent component part of the market , it has more than its fair share of competitor . AMD competes with Intel in the personal computer C.P.U. mart , but also does big business in art processor chips that are popular with PC gamers . Nvidia , famous for its graphics chips , also manufactures CPUs . In 2020 , Apple introduced its grand - serial chip , which are exchange the Intel chips Apple was using for its Macintosh computing machine . Samsungmay also be workingon its own proprietary processor designs . Many more companies build up processor for other electronics usance , like cars and smart abode products . The market is vex more and more competitive .
Microprocessor Logic
To understand how a microprocessor works , it is helpful to look in spite of appearance and get wind about the system of logic used to create one . In the mental process you could also learn aboutassembly spoken communication — the native speech communication of a microprocessor — and many of the things that engineers can do to hike up the speed of a central processing unit .
A microprocessor execute a collection of machine didactics that evidence the processor what to do . Based on the instructions , a microprocessor does three introductory matter :
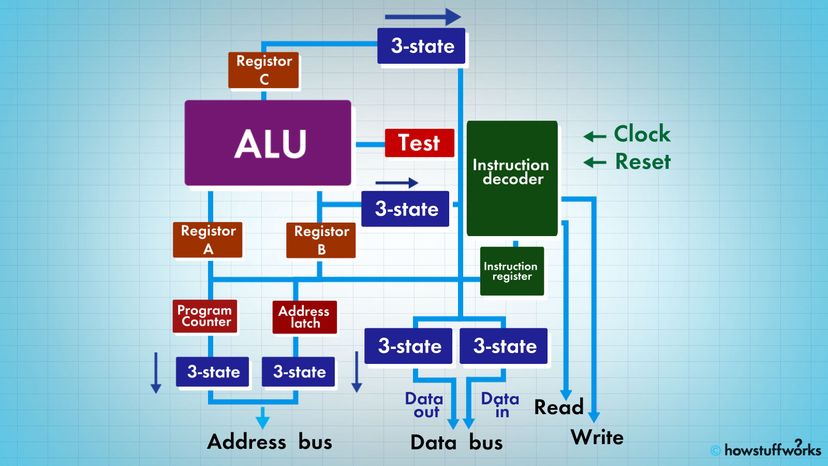
There may be very sophisticated things that a microprocessor does , but those are its three basic natural process . The come after diagram shows an passing simple microprocessor capable of doing those three thing :
This is about as simple as a microprocessor gets . This microprocessor has :
Let ’s put on that both the address and data buses are 8 bits panoptic in this example .
Here are the components of this bare microprocessor :
Although they are not shown in this diagram , there would be mastery channel from the program line decoder that would :
come into the instruction decipherer are the bits from the test register and the clock line , as well as the bits from the instruction cash register .
Microprocessor Memory
The previous section talked about the name and address and data jalopy , as well as the RD and WR lines . These buses and note relate either to RAM or ROM — broadly speaking both . In our sample microprocessor , we have an computer address bus 8 snatch all-encompassing and a data bus 8 bits wide . That means that the microprocessor can address 256 byte of memory , and it can translate or write 8 bit of the memory at a time . permit ’s assume that this childlike microprocessor has 128 bytes of ROM starting at address 0 and 128 byte of RAM start up at address 128 .
ROMstands for read - only memory . A ROM chip is programmed with a permanent collection of pre - set bytes . The address bus tells the ROM silicon chip which byte to get and post on the data bus . When the RD line changes United States Department of State , the ROM microchip presents the selected byte onto the data passenger vehicle .
RAMstands for random - access memory . RAM contains byte of info , and the microprocessor can read or compose to those byte depending on whether the RD or WR line is signal . One problem with today ’s RAM chips is that they forget everything once thepowergoes off . That is why the computer needs ROM .
By the fashion , nearly all electronic computer contain some amount of read-only storage ( it is possible to create a simple computer that incorporate no RAM — manymicrocontrollersdo this by placing a smattering of RAM byte on the mainframe Saratoga chip itself — but generally insufferable to produce one that control no ROM ) . On aPC , the ROM is call theBIOS(Basic Input / Output System ) . When the microprocessor commence , it begins execute instructions it ascertain in the BIOS . The BIOS instructions do things like screen the hardware in the machine , and then it goes to the hard disk to fetch theboot sector(seeHow Hard Disks Workfor point ) . This boot sphere is another modest programme , and the BIOS hive away it in RAM after reading it off the disk . The microprocessor then begins executing the rush sector ’s teaching from RAM . The flush sector program will tell the microprocessor to fetch something else from the hard phonograph recording into RAM , which the microprocessor then run , and so on . This is how the microprocessor load and accomplish the entireoperating organization .
Microprocessor Instructions
Even the implausibly round-eyed microprocessor show in the old example has a pretty large set of didactics that it can perform . The collection of instructions is follow through as bit patterns , each one of which has a different import when load up into the teaching register . Humans are not particularly near at remembering bit pattern , so a set of short Christian Bible are defined to represent the unlike flake patterns . This collection of word of honor is called theassembly languageof the central processor . Anassemblercan translate the words into their routine pattern very well , and then the output of the assembler is placed in memory for the microprocessor to fulfil .
Here ’s the set of gathering language instructions that the decorator might make for the simple microprocessor in our exemplar :
If you have readHow C Programming work , then you know that this simple piece of C code will calculate the factorial of 5 ( where the factorial of 5 = 5 ! = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 120 ):
At the end of the program ’s implementation , the variablefcontains the factorial of 5 .
Assembly Language
AC compilertranslates this C code into assembly language . Assuming that RAM starts at destination 128 in this CPU , and ROM ( which contains the gathering terminology program ) get going at address 0 , then for our simple microprocessor the forum linguistic process might look like this :
ROM
So now the question is , " How do all of these instructions see in ROM ? " Each of these assembly voice communication instructions must be represented by a binary numeral . For the sake of easiness , let ’s bear each assembly language program line is given a unique figure , like this :
The act are get it on asopcodes . In ROM , our little program would look like this :
you could see that seven lines of C code became 18 lines of forum language , and that became 32 bytes in ROM .
Decoding
The instruction decipherer needs to turn each of the opcodes into a circle of sign that drive the dissimilar components inside the microprocessor . permit ’s take the ADD instruction as an example and expect at what it ask to do :
Every instruction can be broken down as a set of sequenced mental process like these that pull wires the element of the microprocessor in the proper order . Some book of instructions , like this ADD instruction , might take two or three clock wheel . Others might take five or six clock cycles .
Microprocessor Performance and Trends
The number oftransistorsavailable has a huge essence on the public presentation of a processor . As seen originally , a distinctive teaching in a processor like an 8088 took 15 clock cycle to carry out . Because of the design of the multiplier , it shoot around 80 cycles just to do one 16 - bit multiplication on the 8088 . With moretransistors , much more hefty multipliers subject of unmarried - cycle focal ratio become possible .
More transistors also grant for a technology calledpipelining . In a pipelined computer architecture , instruction death penalty overlaps . So even though it might take five clock bike to fulfil each instruction , there can be five instructions in various degree of execution simultaneously . That way it looks like one instruction completes every clock cycle .
Many modern central processing unit have multiple instruction decoders , each with its own pipeline . This allow for multiple instruction stream , which means that more than one instruction can fill out during each clock cycle . This proficiency can be quite complex to implement , so it takes lots of transistor .
Trends
These twenty-four hours it seems like processors are everywhere , and that trend does n’t appear to be slowing . Researchers have happen slipway tomake microprocessor flexible , enable item such assmart article of clothing . researcher have been work on ways to uselight , rather than electricity , to go processor . Probably the biggest alteration on the horizon is the development of quantum computers , which are n’t restricted to using 1s and 0s to solve problem . While these computers canprocess more unmanageable problemsmore efficiently , it ’s unlikely you will see a quantum computer on your desktop anytime soon .
64-bit Microprocessors
Sixty - four - bit central processor have been with us since 1992 , and in the 21st century they have become mainstream . These processor have 64 - bit ALUs , 64 - bit register , 64 - bit motorcoach and so on .
One ground why the world need 64 - bit processors is because of theirenlarged computer address spaces . Thirty - two - second chips are often constrained to a maximum of 2 GB or 4 GB ofRAM admittance . That seemed like a lot when most home computers used only 256 MB to 512 MB of random-access memory . But 21st - century home computing machine can process information ( very complex data features hatful of genuine numbers ) quicker . multitude doingvideo editingand masses doing photographic editing on very bombastic image profit from this form of computing big businessman . High - end gamers also benefit from more elaborate eminent - resolution games .
A 64 - bit chip open up up more pick because a 64 - bit Aries the Ram address space is essentially infinite for the foreseeable future tense — 2 ^ 64 bytes of RAM is something on the orderliness of a billion gigabytes of RAM . With a 64 - bit address jalopy and wide-eyed , eminent - amphetamine data charabanc on themotherboard , 64 - bit machine also proffer quicker I / atomic number 8 ( input / output ) speeds to things likehard disc drivesandvideo carte du jour . These feature can greatly increase organization performance .
For more selective information on microprocessor and related subject , delay out the follow connectedness .