Types of OLEDs: Transparent, Top-emitting, Foldable and White
Transparent OLED
Transparent organic light-emitting diode have only transparent components ( substrate , cathode and anode ) and , when turned off , are up to 85 percent as sheer as their substrate . When a vapourous OLED exhibit is turned on , it allows light to pass in both direction . A transparent OLED display can be either active- or peaceful - matrix . This technology can be used for heads - up displays .
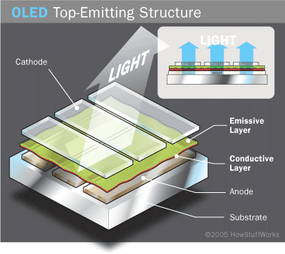
Top-emitting OLED
Top - breathe OLEDs have a substratum that is either opaque or reflective . They are best suited to fighting - matrix design . Manufacturers may use top - emitting organic light-emitting diode exhibit insmart cards .
Foldable OLED
Foldable organic light-emitting diode have substrate made of very whippy metal foils or plastics . Foldable OLEDs are very lightweight and perdurable . Their use in devices such as cellular telephone phone and PDAs can reduce breakage , a major cause for return or repair . Potentially , foldaway OLED displays can be attached to fabrics to make " smart " clothing , such as outdoor survival of the fittest clothing with an integrated computing gadget chip , cellphone headphone , GPS receiver and OLED video display sewn into it .
White OLED
White OLEDs emit white light that is bright , more uniform and more energy efficient than that breathe byfluorescent lights . whitened organic light-emitting diode also have the true - coloring material calibre ofincandescent lighting . Because OLEDs can be made in enceinte canvas , they can supplant fluorescent lights that are currently used in homes and building . Their use could potentially thin out free energy price for lighting .
In the next section , we ’ll talk over the pro and cons of OLED engineering science and how it compares to steady LED and LCD technology .