Electromagnetic wireless wavesare one of the most significant breakthrough for twentieth and twenty-first century technology . You do n’t see them , but infinite high frequency waves are bouncing through the tune around you every solar day . They ease wireless communication for thing like car wireless , smartphones , and Wi - Fi cyberspace . Thanks to radio , data transmitting between hoi polloi is faster and more convenient than ever .
Here are just a few of the everyday engineering science that depend on wireless undulation :
Even things likeradarandmicrowave ovensdepend on radio receiver waves . Communication and pilotage satellites would be inconceivable without radio waves , as would innovative air power — an airplane depend on a dozen different wireless system . TheWiFi networksthat we count on at work , family and school also trust completely on radio waves for information transmittance .
The funny thing is that , at its kernel , wireless is an incredibly uncomplicated technology . With just a couple of electronic part that be at most a dollar or two , you’re able to build simple radio transmitters and receivers . In this article , we will explore the technology of radio so that you’re able to altogether understand how invisible radio waves make so many thing possible .
The Simplest Radio
Radio can be fabulously dim-witted , and around the turn of the 20th hundred this simpleness made other experimentation possible for just about anyone . How round-eyed can it get ? Here ’s an lesson :
Yourbattery / coin combinationis a wireless transmitter ! It ’s not transmitting anything useful ( just inactive ) , and it will not carry very far ( just a few in , because it ’s not optimized for aloofness ) . But if you use the static to rap out Morse codification , you may really communicate over several in with this rough equipment .
A (Slightly) More Elaborate Radio
If you want to get a little more luxuriant , use a metal filing cabinet and two pieces of wire . Connect the handle of the file to one terminal of your 9 - volt battery . link the other part of wire to the other terminus and execute the free end of the wire up and down the file cabinet . If you do this in the shadow , you will be able to see very small 9 - volt sparks running along the file as the crest of the conducting wire connects and disconnect with the file ’s ridges . Hold the file near an AM tuner and you will see a plenty of atmospheric static .
In the early day of radio , the transmitters were calledspark coils , and they create a continuous current of sparks at much higher electromotive force ( e.g. 20,000 volts ) . The high electromotive force created big fat spark like you see in aspark plug , and they could transmit far . Today , a transmitter like that is illegal because it spams the entireradio spectrum , but in the early days it worked fine and was very common because wireless waves were not intemperately regulated .
Radio Basics: The Parts
As seen in the previous section , it is fantastically well-to-do to channel with static . All radios today , however , usecontinuous sine wavesto transmit data . Very early radio sender utter a expectant band of frequencies at once . All they could procreate were elementary noises which could be used to pass on with Morse code . A sine waving transmitter narrows this band down to more specific relative frequency which can effectively reproduce complex data like audio stream , picture and internet data point . The narrow frequency banding also permit many transmitter to operate in an area without interfering with one another .
We use uninterrupted sine waves today is because there are so many different citizenry and machine that want to use tuner waves at the same time . If you had some way to see them , you would find that there are literally M of unlike wireless wave ( in the chassis of sine moving ridge ) around you right now — television broadcasts , AM and FM radio broadcasts , police and fire radio , satellite TVtransmissions , cell phone conversations , GPSsignals and so on . It is awe-inspiring how many usage there are for radio set waves today . Each different radio signaling uses a unlike sine wave absolute frequency , and that is how they are all separated .
Anyradio setuphas two parts :
The sender lead some sort of subject matter ( it could be the phone of someone ’s vocalisation , pictures for aTV solidification , datum for a radio modem , etc . ) , encodes it onto a sine wave and impart it with radiocommunication wave . The liquidator receive the radio waves and decodes the message from the sine wave it receives . Both the transmitter and receiver use antenna to glow and capture the wireless signal .
Simple Transmitters
you may get an idea for how a radio transmitter work bystarting with a battery and a piece of wire . A battery institutionalize electricity ( a stream of electrons ) through a wire if you plug in the wire between the two depot of the battery . The prompt electrons make a magnetized field surrounding the wire , and that field is stiff enough to impact a range .
have ’s say that you take another wire and place it parallel to the barrage fire ’s conducting wire but 2 inches ( 5 centimeters ) forth from it . If you connect a very sensitive voltmeter to the telegram , then the chase will chance : Every time you connect or disconnect the first telegram from the assault and battery , you will sense a very small-scale electric potential and current in the second wire ; any changing magnetic field can bring on an electric field in a music director — this is the canonic principle behind any electric author . So :
One important thing to notice is that electrons flow in the second conducting wire only when you link up or disconnect the battery . A magnetic discipline does not cause electrons to hang in a wire unless the magnetic field of force is deepen . Connecting and unplug the battery changes the magnetized field ( connecting the electric battery to the wire create the charismatic field , while disconnect collapses the field of force ) , so electrons flow in the second wire at those two moment .
Making Your Own Simple Transmitter
To create a elementary wireless sender , what you need to do is create a chop-chop alter electric current in a conducting wire . you could do that by quickly connecting and disconnecting a shelling , as shown at left hand :
A better way is to create a continuously varying galvanising current in a telegram . The mere ( and smoothest ) form of a continuously motley moving ridge is a sine wave like the one testify below :
By creating a sine wave and running it through a wire , you create a simple wireless vector . It is extremely easy to make a sine wave with just a few electronic component — acapacitorand aninductorcan create the sine undulation , and a couple of transistors can magnify the wave into a powerful andsimple vector formal . By air that signaling to an antenna , you may transmit the sine wave into space .
Transmitting Information
If you have a sine wave and a transmitter that is transmitting the sine wave into outer space with an antenna , you have a radio station . The only trouble is that the sine wave does n’t take any selective information . You postulate to regulate the wave in some style to encode information on it . There are four common ways to modulate a sine wave :
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
In PWM , you but turn the sine wafture on and off . This is an well-heeled way to send Morse code . PWM is not that common , but one near example of it is the radio set system that sends sign toradio - controlled clocksin the United States . One PWM transmitteris able to insure the entire United States !
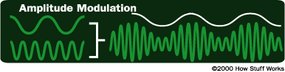
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
AM radio stations useamplitude modulationto encode information . In amplitude modulation , the amplitude of the sine waving ( its peak - to - peak electric potential ) change . So , for lesson , the sine wafture produced by a person ’s voice is overlaid onto the transmitter ’s sine wave to vary its bountifulness .
Frequency Modulation (FM)
FM radio stations and century of other wireless technologies usefrequency intonation . The advantage to FM is that it is mostly immune to static . In FM , the transmitter ’s sine wave frequence change very somewhat base on the info signal . FM uses higher frequency signals than AM , which have high fidelity but a step-down in range .
Digital Modulation
Digital intonation encodes digital information onto an analogue carrier signaling and provides gamy faithfulness without any of the distinctive static . In the case of things like wireless routers , digital inflection also allows the sign to be write in code . This way , the transmitter will only send data to particular gimmick .
However , a digital signaling that is too watery will rapidly become unusable . Audio information will go scrambled , and TV will be extremely pixelated . In the U.S. over - the - air television has moved alone over to digital transmission , and many terrestrial radio station operate on digital antennas in addition to their parallel signal .
Once you tone a sine wave with information , you’re able to transmit the information .
Receiving an AM Signal
Here ’s a literal - world deterrent example . When you tune up your car ’s AM radio to a station — for example , 680 on the AM dial — the transmitter ’s sine wave is transmit at 680,000 hertz ( the sin wave repeats 680,000 times per secondly ) . The DJ ’s vocalisation is modulated onto that carrier wave wave by varying the amplitude of the sender ’s sine wave . An amplifier amplifies the signal to something like 50,000 watts for a large AM place . Then the antenna sends the wireless waves out into outer space .
So how does your machine ’s AM radio — a receiver — receive the 680,000 - Gustav Hertz sign that the sender sent and extract the information ( the DJ ’s voice ) from it ? Here ’s how it works./\r\n/
What you hear coming out of the speakers is the DJ ’s voice !
In an FM radio , the detector is different , but everything else is the same . In FM , the sensing element turn over the changes in oftenness into sound , but the antenna , tuner and amplifier are largely the same .
The Simplest AM Receiver
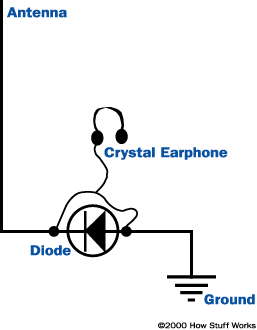
In the pillow slip of a strong AM signal , it turns out that you may create asimple radio receiverwith just two part and some conducting wire . The procedure is extremely elementary — here ’s what you require :
To make the outgrowth easier , some kits are also uncommitted online contain most of the necessary parts in the box . TheHome Science Tools crystal radio kitalso come with an galvanising amplifier , cause the earphone unneeded .
You now demand to obtain and be near an AM tuner post ’s transmitting tower ( within 1 mile/1.6 kilometer or so ) for this to work . Here ’s what you do :
Now if you put the earplug in your capitulum , you will hear the radio station — that is the simple possible radio receiver ! This super - simple project will not work if you are very far from the place , but it does march how unproblematic a radio liquidator can be .
Here ’s how it works . Your telegram antenna is receive all sort of radio receiver signals , but because you are so tight to a picky transmitter it does n’t really matter . The nearby signal overwhelms everything else by a factor of millions . Because you are so close to the sender , the feeler is also receiving lots of zip — enough to repulse an earphone ! Therefore , you do n’t call for a radio receiver or batteries or anything else . The diode acts as a detector for the AM signaling as account in the previous section . So , you may learn the station despite the lack of a tuner and an amplifier . However , adding an amplifier like that on the educational kit will further the signaling and give it heavy loudness .
Antenna Basics
You have probably notice that almost every wireless you see ( like your cell speech sound , the radio in your elevator car , etc . ) has anantenna . antenna come in all shape and size of it , depending on the frequency the aerial is trying to receive . The feeler can be anything from a longsighted , potent wire ( as in the AM / FM receiving set antennas on car ) to something as bizarre as asatellite lulu . wireless transmitters also use extremely tall antenna towers to transmit their signal .
The mind behind an antenna in a wireless sender is to launch the radio waves into space . In a liquidator , the estimation is to piece up as much of the transmitter ’s power as potential and provide it to the tuner . For satellites that are millions of land mile away , NASAuseshuge dish antennasup to 230 foot ( 70 meters ) in diam .
The sizing of an optimum radio receiver antenna is have-to doe with to the frequency of the sign that the feeler is trying to transfer or meet . The reason for this relationship has to do with the speed of light , and the distance negatron can travel as a resultant role . Thespeed of lightis 186,000 miles per second ( 300,000 kilometers per secondly ) . So , how do you know what sizing antenna you ask ?
Antenna: Real-life Examples
Let ’s say that you are trying to build a radio tug for radio station 680 AM . It is channel a sine wave with a oftenness of 680,000 hertz . In one Hz of the sin wave , the transmitter is snuff it to move electrons in the antenna in one focus , switch and pull them back , switch and push them out and switch and move them back again . In other words , the electron willchange direction four timesduring one cps of the sine undulation . If the transmitter is running at 680,000 hertz , that mean that every cycle fill in in ( 1/680,000 ) or 0.00000147 seconds . One quarter of that is 0.0000003675 second .
At the speed of light , negatron can move 0.0684 miles ( 0.11 kilometers ) in 0.0000003675 seconds . That think of the optimum aerial size of it for the sender at 680,000 Heinrich Hertz is about 361 foot ( 110 meters ) . So , AM wireless station demand very tall towers . For a cadre phone working at 900,000,000 ( 900 megacycle ) , on the other hand , the optimum transmitting aerial size is about 3 inch or 8.3 centimeters . This is why cadre phones can have such short antennas .
You might have noticed that the AM radio antenna in your car is not 300 feet ( 91 meters ) long — it is only a couple of ft long . If you made the aerial longer it would have better , but AM post are so strong in city that it does n’t really matter if your antenna is the optimal duration .
You might wonder why , when a radio sender transmit something , radio waves want to propagate through space out from the feeler at the upper of light . Why can radiocommunication waves jaunt millions of miles ? Why does n’t the antenna just have a magnetic field of force around it , confining to the aerial , as you see with a wire attached to a battery ? One unsubdivided way to think about it is this : When current participate the antenna , it does create a magnetic field around the feeler .
We have also seen that the magnetised field of view will make an electric field ( electric potential and current ) in another wire come in near to the transmitter . It turn out that , in quad , the magnetised field create by the aerial stimulate an electric field in quad . This electric field in bout induce another magnetic field in blank space , which induce another galvanic field , which induces another magnetised field of battle , and so on . These galvanizing and magnetic fields ( electromagnetic field ) induce each other in space at the speed of spark , jaunt outward away from the antenna .
Analog vs. Digital Radio
Although analog radio sources are still pervasive , digital sign like Wi - Fi and Bluetooth have taken over . In 2009,the U.S. mandatedthat the bulk of over - the - air analog TV stations would have to switch to digital transmitters . For many radio Stations of the Cross , a digital formatting known asHD Radiois also available . However , FM sign remain the current criterion , probable because a large act of older vehicles on the road still rely on AM / FM tuners .
The advantages provided by adigital radio transmissionare faithfulness and surety . Digital signaling carry the much higher datum pace needed to supply things like high - definition picture or wireless internet . The receiver also gets none of the disturbance and static that is ever - present in analog transmissions . However , theactual method acting of transmissioncan get complicated .
Since radio wave are a traditional analog signal , the transmitter needs to convert its data using adigital to analog convertor . Once the receiving feeler pick up the signal , it then has to " unscramble " the datum back to its original descriptor using an analog to digital converter . This method go overly complex , but it does allow for thing likedata encryption .
Essentially , the encounter antenna must have the right educational activity to unknot the digital data that was converted by the transmitter . Without those instructions , the data can not be accessed . This is why people generally ca n’t access your Wi - Fi or bluetooth without mate with the correct gadget . This appendage also helps cut down on tuner hinderance in the air . analogue radio signals , on the other hired man , can be accessed by anyone in the area with a functioning antenna .