If you have take the HowStuffWorks articleHow router Work , then you lie with that a router is used to manage web traffic and find the best route for transport packets . But have you ever thought about how routers do this ? Routers require to have some information about net status in purchase order to make decisions regarding how and where to send packet . But how do they gather this information ?
In this article , we ’ll find out precisely what data is used by routers in determining where to send a mailboat .
The Basics
Routers userouting algorithmsto find the ripe path to a destination . When we say " right road , " we consider parameters like the number ofhops(the trip a packet boat assume from one router or intermediate point to another in the meshing ) , sentence delay and communication toll of packet transmitting .
Based on how routers cumulate entropy about the structure of a internet and their analytic thinking of information to specify the estimable route , we have two major routing algorithms : world routing algorithmsanddecentralized spreadeagle algorithms . In decentralised spreadeagle algorithmic program , each router has selective information about the routers it is directly connected to – it does n’t know about every router in the internet . These algorithms are also make out asDV(distance transmitter ) algorithms . In global routing algorithmic rule , every router has complete information about all other routers in the web and the traffic condition of the web . These algorithms are also known asLS(link state ) algorithm . We ’ll talk over LS algorithms in the next subdivision .
LS Algorithms
In LS algorithmic rule , every router has to follow these step :
TheDijkstra algorithmgoes through these steps :
We will practice this algorithm as an example on the next Thomas Nelson Page .
Example: Dijkstra Algorithm
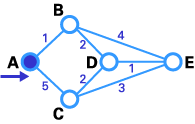
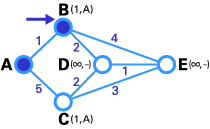
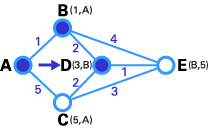
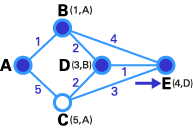
Here we want to find the best route between A and E ( see below ) . you may see that there are six potential routes between A and E ( ABE , ACE , ABDE , ACDE , ABDCE , ACDBE ) , and it ’s obvious that ABDE is the good route because its weighting is the lowest . But sprightliness is not always so sluttish , and there are some complicated cases in which we have to apply algorithmic program to happen the undecomposed itinerary .
in conclusion , E is the destination , so we stop here .
We are at end ! Now we have to discover the route . The old node of E is 500 , and the previous node of D is barn , and B ’s late thickening is A. So the best route is ABDE . In this case , the total weigh is4(1 + 2 + 1 ) .
Although this algorithm work well , it ’s so complicated that it may take a farseeing metre for router to process it , and the efficiency of the connection fails . Also , if a router give the wrong selective information to other routers , all routing decisions will be ineffective . To understand this algorithm better , here is the source of program compose by C :
DV Algorithms
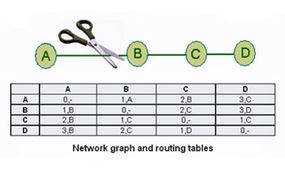
DV algorithms are also be intimate as Bellman - Ford gouge algorithm and Ford - Fulkerson route algorithms . In these algorithmic rule , every router has a routing table that shows it the near path for any finish . A typical graphical record and routing board for router J is shown at the top of the varlet .
As the tabular array shows , if router J wants to get mail boat to router D , it should transport them to router H. When packets arrive at router H , it check its own table and adjudicate how to send out the packet to D.
In DV algorithms , each router has to take these steps :
One of the most important problems with DV algorithm is called " numeration to infinity . " lease ’s essay this problem with an example :
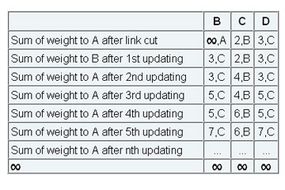
Imagine a internet with a graph as indicate below . As you see in this graph , there is only one link between A and the other parts of the net . Here you’re able to see the graph and route table of all node :
Now imagine that the data link between A and B is cut . At this time , B redress its mesa . After a specific amount of time , routers commute their table , and so B pick up C ’s routing table . Since C does n’t know what has befall to the link between A and B , it says that it has a link to A with the weighting of 2 ( 1 for degree centigrade to B , and 1 for atomic number 5 to A – it does n’t know barn has no link to A ) . B receive this table and believe there is a separate tie-in between C and A , so it corrects its table and changes infinity to 3 ( 1 for B to C , and 2 for atomic number 6 to A , as C order ) . Once again , routers exchange their table . When C encounter B ’s routing board , it determine that B has changed the system of weights of its tie to A from 1 to 3 , so C updates its tabular array and change the exercising weight of the link to A to 4 ( 1 for 100 to B , and 3 for B to A , as B said ) .
This process loops until all nodes determine out that the weighting of connection to A is eternity . This situation is shown in the board below . In this elbow room , experts say DV algorithm have aslow convergency rate .
One path to solve this trouble is for routers to send data only to the neighbour that are not exclusive links to the destination . For example , in this example , C should n’t send any info to B about A , because B is the only way to A.
Hierarchical Routing
As you see , in both LS and DV algorithms , every router has to save some entropy about other router . When the meshing size rise , the number of routers in the connection increases . Consequently , the size of routing tables increases , as well , and router ca n’t handle web traffic as expeditiously . We usehierarchical routingto overcome this trouble . countenance ’s examine this content with an example :
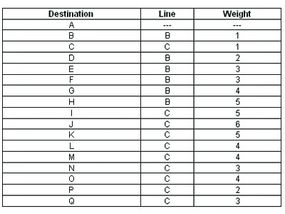
We use DV algorithmic program to find expert road between nodes . In the situation depicted below , every node of the electronic internet has to save a routing board with 17 records . Here is a typical graphical record and routing board for A :
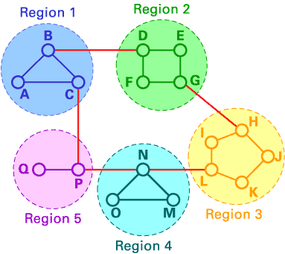
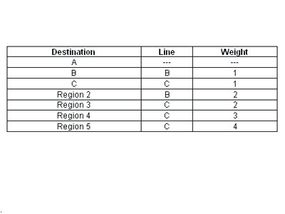
In hierarchal routing , routers are classify in groups get laid asregions . Each router has only the entropy about the router in its own region and has no data about routers in other region . So routers just save one disc in their table for every other neighborhood . In this example , we have classified our connection into five regions ( see below ) .
If A wants to place packets to any router in part 2 ( viosterol , E , F or G ) , it commit them to B , and so on . As you may see , in this character of routing , the tables can be summarise , so web efficiency meliorate . The above exemplar shows two - grade hierarchical routing . We can also utilize three- or four - level hierarchal routing .
In three - level hierarchical routing , the web is classified into a phone number ofclusters . Each cluster is made up of a telephone number of regions , and each region contains a issue or router . Hierarchical routing is widely used in Internet routing and makes use of several routing protocol .
For more entropy on expel and related topic , look into out the links on the next page .
Frequently Answered Questions
Lots More Information
Related Articles
More Great Links
Roozbeh Razavi is a student of electronic engineering at K.N.T University of Technology . He is also a transcriber of the book " Networking Essentials Plus , " by Microsoft Corporation . His study have focused on areas of TCP / IP , routing and web security .