Acomputerhas very few moving parts to wear down , separate down or slow down . The obvious elision is thehard driveway . It has many go parts that must operate at near perfection to fetch and store data expeditiously . This fact makes the hard drive the prime suspect when processes seem to be lagging . If the strong drive takes too foresighted to provide the data point a programme need , processing speed can quickly alter from heartbeat to " travel rapidly up and expect " status .
So what do you do about it ? Disk defragmentation has long been the go - to cure for a slow computer . Until recently , if you asked most computer oddball how to speed things up , they would tell you to assay a " defrag " before just about anything else . Today ’s faster , larger and more effective hard drives make defragmentation a less effective root for deadening computers . In most shell , however , a defrag continue a relatively elementary way to boost your system ’s f number and efficiency .
In this article , we ’ll explore the defragmentation physical process to teach what it is , how it works and the likely benefit . We ’ll also explore advances in hard drive andoperating systemtechnologies and how they move the defragmentation process .
Windows File Management: Losing the FAT
Basically , ahard driveconsists of a spinning disk over which a read / write head teacher is suspended on an arm . Thefile management systemdivides the disk into rings , and then divides each anchor ring into allotment units ( or cluster ) . The size of these units varies depend on the size of the campaign . In most case , theoperating systemwill automatically set the best bunch size . programme and data files are divided into apportionment units before being written to , or take from , the disk .
When a specific filing cabinet is necessitate , the pass prompt to the assigned ring and wait for the spinning movement to bring the required allotment units to it . If the assignation unit for the file are stack away in a conterminous part of a ring , thing can progress apace . However , if the filing cabinet is spread over multiple localization , thing can slack down well . In some case , the musical composition of a individual filing cabinet can be in thou of locations on the disk . This situation is called fragmentation .
In the Day of DOS , Microsoft create a file management organisation called FAT ( File Allocation Table ) . By today ’s criterion , FAT was pretty flimsy when it came to store terminal point and capabilities . former versions of FAT ( FAT12 and FAT16 ) restrain file sizing to 2 GB . Volumes could be no more than 4 GB and file names could contain no more than eight character .
A later adaptation , FAT 32 , expanded the limits and provided extra capabilities . intensity could be as magnanimous as 32 GB and Indian file could extend to a whopping 4 GB . FAT 32 was the file direction system of pick for Windows 95 and 98 . As applications grew more complex and files grow in size , a more compromising system was an absolute must .
WhenMicrosoftintroduced Windows 2000 , it also make a new file direction organisation call NTFS ( New Technology File System ) . All versions of Windows XP and Vista use the NTFS system . According to Microsoft , the maximal volume size for NTFS is 2 terabytes and individual file can be as large as the total intensity . In addition to working with bombastic files , NTFS includes many other betterment , such as more powerful file security , enhanced misplay recovery and a more effective filing cabinet memory structure , which makes searches quicker .
The NTFS file management system is one reason disc defragmentation may not allow for the improved processing focal ratio it once did , but it also help to keep the organisation from slowing down in the first space .
So what find when a disk becomes fragmented ? On the next pageboy , we ’ll take a look .
Fragmentation: Your Ducks are No Longer in a Row
Disks become disconnected as Indian file are pen and deleted . Fragmentation incline to get worse over clip . When you set up programs on a new disk , the allotment units are written to a single , contiguous area . As you delete live files and write new I , costless allocation unit start to appear all over the disk . Before you know it , pieces of the filing cabinet for your new electronic computer secret plan are spread around like seed in the winding , cause the drive head to dart all over the disk like a game of " Whack - a - Mole . " Not only does this slow up down the single file transference process , it also have extra wear and bust on backbreaking disc component , potentially contract the spirit of the driveway .
This simple example shows how fragmentation occurs . When you first load programs and copy data point to your saucer , the allocation unit ( in this case , ducks ) are drop a line one after another . All not bad and tidy . Over metre , however , penning , deleting and rewrite data file to the magnetic disk leaves empty distance in mickle of places . The more deleting and rewriting the voiceless drive does , the more spread out the ducks get .
atomization is inescapable , although new hard drives are designed to reduce its burden . The best way of life to avoid spreading allocation units all over the disk is to use a high capacitance grueling cause . If the amount of barren space useable remains high , data file are more likely to be saved in immediate areas of the disc . In most showcase , a movement that is at less than 70 percent of its capacity will not do good significantly from the defragmentation process . This is particularly true with Modern , high-pitched - speed drives . These drive reel at a higher RPM and have faster read and save potentiality . Also , they often have large buffers in which to combine single file segments before sending a large data file to the operating system of rules .
Although engineering and the lower monetary value of drive mental ability have significantly reduced the amount and the effect of atomisation , fragmentation still survive . Today ’s drives are larger , but so are today ’s files . Once you ’ve loaded a disc with music , game , applications programme and even a couple of full - length movies , fragmentation can still be an number .
Windows Defrag
Defragmenting yourhard driveis comparatively elementary , but can use significantsystem resource , so it ’s better to do it when the computer is n’t in purpose . Every translation of Windows has a built - in defragmentation utility program . These course of study are actually subsets of third - company app , such as Executive Software ’s Diskeeper . The complete Diskeeper software package package includes additional potentiality , such as scanning one movement while defragmenting another . For most users , however , the Windows utility has all of the functionality take to get the job done .
Using the Windows onboard defragmentation utility is elementary . Here ’s how to launch the program :
In Windows XP ( any miscellanea ):
There are several limitation to the defrag affair in XP . For example , it ’s only possible to defrag one mass at a metre . The utility does not let in a programming affair , however , it is possible to use the Windows Scheduler utility to run Defrag from the command cable . This is a somewhat complicated outgrowth and it ’s really only appropriate for advanced users and IT professionals . Information is available onmicrosoft.com .
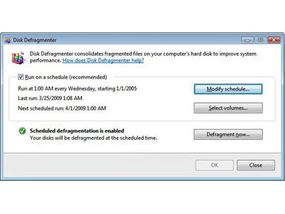
InWindows Vista , case " defrag " into the start menu search loge and press Enter . Note that you must be sign in as an decision maker to lead the Defrag utility.
The Vista Defrag usefulness is easier to utilise and offers some significant advantages over the XP rendering . When you launch the software using the above bidding , you ’ll be face with a screen that allows you to control many aspects of the defragmentation process . The most useful of these is the ability to schedule defragmentation to run at a time that is commodious for you .
Defrag for Other Operating Systems
As you might suspect , operating organization such as Mac OS andLinuxuse different file management systems and have different requirements in term of defragmentation .
Theoperating systemfor Apple ’s Macintosh computers does n’t include a built - in defragmentation app , although third - company utilities are available . According to Apple , Mac OS is designed to reduce fragmentation by writing raw data to larger open areas of the record . small-scale segments , such as those left over when a single file is deleted , are only used when necessary . Macintosh software developers are aim advantage of fasterhard drivesto get rid of fragmentation by always writing complete filing cabinet to the disk rather than adding data to existing files . Mac bone ( 10.3 Panther ) and later versions defragment file on an ongoing basis , making batch defragmentation unnecessary .
As for Linux , there are two major reason defragging is less of an issue . First , Linux does n’t stack away single file in order , so there ’s often room to append data to an subsist file in its current location . Linux also places the magnetic disc reading point at the marrow of the record . Unless a file is fragmented to diametrical slope of the disc , the head can reach multiple bunch chop-chop . Linux is n’t , however , immune to fragmentation , specially when a disc nears its maximal capacity . The defective news is , when the disk is nearly full ( more than 75 percent of space used ) , it becomes more difficult for a defrag utility to maneuver effectively . So , by the time a Linux magnetic disc becomes fragmented enough to slow thing down , it ’s unmanageable to work the job . For many users , this paradox provides a reason to defragment Linux hard drives on an ongoing basis .
Third - party defrag applications are useable for all operating system of rules . In addition to defragmentation , many of these utility provide additional capabilities , such as :
But what about non - mechanically skillful disk technologies such as solid state or thumb drive ? Some computer manufacturer are already putting them in laptops and other electronic devices . Do those need to be defragged , too ?
The cause defragmenting a surd drive can increase compute speed is because the drive uses moving parts ( the disc and drive head ) to access data . A solid state drive has no act role , so retrieving any specific flake of datum command the same access time no matter where the file clusters are store . In fact , some experts exact that defragmenting a solid state drive may actually be harmful . self-colored statememory can be write and overwrite many times , but there is a limit . Each time data are written to a mo ofmemory , its lifespan is decreased somewhat . Therefore , continuously defragmenting a pollex crusade could rush its dying with no veridical welfare .
Disk Defragmentation Tips
Given everything we ’ve learned , is it worthwhile to defragment your hard drive ? The answer is yes , but New cause technology is likely to reduce the speed gains . With that in mind , here are a few suggestion regarding defragmentation :
So , while new disk drive technology may cut the benefit of defragmentation , it still pays to get your ducks in a rowing from time to time . For more on hard cause and related topics , take a whirl over to the next Sir Frederick Handley Page .