When it comes tohome theater of operations , a pile of people guess big – a giving picture and lots of sound coming from a widescreenTVand an raiment ofspeakers . But the typical household - theater apparatus , with itssurround - soundspeakers and subwoofer , wo n’t work for every plate . Some hoi polloi do n’t have enough elbow room for all of that equipment . Others do n’t require their living room littered with cable , or they do n’t need the rough-and-tumble of line up the positioning and elevation of lots of speakers .
That ’s wherevirtual surround soundcomes in . It mimics the effect of a multi - speaker surround - sound system , but it apply few speakers and fewer cables . These organisation occur in two primary diverseness –2.1 surroundanddigital sound expulsion . Most of the time , 2.1 - environment systems use two utterer placed in front of the listener and a subwoofer placed somewhere else in the elbow room . These recreate the effect of a 5.1 surround - sound system , which has five speakers and a subwoofer . Digital healthy projectors , on the other hand , tend to employ a single strip of small speakers to acquire sound . Many digital phone projector do not admit a subwoofer .
disregarding of their accurate setup , these systems work on the same canonic rationale . They use a number of technique to modify sound waves so that they seem to come from more speakers than are really there . These techniques come from the study ofpsychoacoustics , or the way in which people perceive audio . In this clause , we ’ll explore the traits of human audience that leave two utterer to sound like five , as well as what to keep in mind if you denounce for a practical environment - sound system .
Perceiving Sound
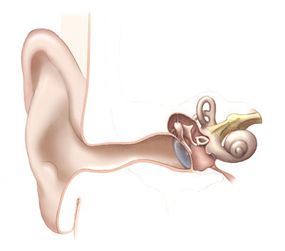
Virtual environs - sound systems take advantage of the basic properties of speakers , sound waves andhearing . A speaker is essentially a gadget that change electric impulses into sound . It does this using adiaphragm– a cone that rapidly move back and forth , pushing against and pulling away from the air next to it . When the diaphragm prompt outward , it make acompression , or area of high pressing , in the air . When it moves back , it creates ararefaction , or arena of lower pressure . you could hear more about the details inHow Speakers Work .
condensation and rarefactions are the result of the movement ofair particles . When the particles push against each other , they create an area of high pressure . These particles also crusade against the molecules next to them . When the speck move aside , they make an surface area of lower pressure while pulling away from the neighboring particles . In this manner , the compressing and rarefactions move through the air as alongitudinal wave .
When this wave of high- and low - pressing areas gain your ear , several things happen that allow you to perceive it as sound . The undulation reflects off of thepinna , or external cone cell , of your spike . This part of your spike is also known as theauricle . The sound also travels into yourear duct , where it physically move yourtympanic tissue layer , or eardrum . This set off a range of mountains chemical reaction involving many tiny structures inside your pinna . Eventually , the vibrations from the wave of air pressure hand yourcochlear nerve , which acquit them to the brain ( brain.htm ) as nerve nervous impulse . Your encephalon represent these impulses as reasoned . How Hearing Works ( hearing.htm ) has stacks more info about your ear ’s intimate structures and what it postulate to perceive sound .
Your mentality ’s version process allows you to understand the sound ’s meaning . If the sound is a series of spoken words , you’re able to put them together into an understandable sentence . If the sound is a Sung , you could translate the Word , experience the tone and regular recurrence , and resolve whether you like what you learn . you may also remember whether you ’ve heard the same Song dynasty or similar songs before .
In addition to allow you to interpret the audio , your brain also uses lots ofaural cuesto assistance you figure out where it come from . This is n’t always something you think about or are even consciously aware of . But being capable to locate the source of a sound is an authoritative acquirement . This ability help animals locate solid food , avoid predatory animal and find others of their metal money . Being capable to tell where a speech sound come from also helps you resolve whether someone is follow you and whether a rap outside is at your door or your neighbour ’s .
These cues and the physical properties of profound waves are cardinal to practical surroundings speech sound . We ’ll seem at them in more detail next .
Sound Cues and Virtual Surround Sound
Most multitude have had the experience of sitting in a very quiet room , like a classroom during a test , and having the muteness break by an unexpected haphazardness , like change falling from someone ’s pocket . ordinarily , multitude straight off turn their caput toward the origin of the phone . turn toward the sound seems almost instinctive – in an instant , your brain determines the sound ’s location . This is often true even if you may only hear in one ear .
A person ’s ability to nail a sound ’s location comes from the wit ’s analysis of the audio ’s attributes . One attribute has to do with the deviation between the sound that your right wing ear discover and the sound that your left ear see . Another has to do with the interactions between the sound waves and your head and body . Together , these are the aural cue that the mind uses to figure out where a sound came from .
Imagine that the coins in our placid classroom model arrive at the story somewhere to your right . Because the audio travels as physical waves through the air – a process that takes meter – it reaches your correct auricle a fraction of a second before it reaches your left . In addition , the sound is a slight quieter by the time it reached your left ear . This decrease in volume is because of the natural dissolution of the sound wave and because your head absorbs and speculate a little bit of the audio . The difference in volume between your left and right ears is theinteraural stratum dispute ( ILD).The delay is theinteraural time difference ( ITD ) .
Time and level difference give your genius a clear estimation of whether a sound came from your left or your right wing . However , these differences carry less entropy about whether the sound come from above you or below you . This is because change the aggrandisement of a sound affects the path it consider to reach your ear , but it does n’t touch on the departure between what you hear in your left and right spike . In improver , it can be hard to figure out whether a sound is arrive from in front of you or behind you if you ’re only relying on time and level difference . This is because , in some case , these sounds can bring on monovular ILDs and ITDs . Even though the sounds are coming from a different placement , thedifferencesin what your ears take heed are still the same . The ILDs and ITDs are identical in a cone - form area put out outwards from your ear known as thecone of confusion .
ILDs and ITDs want mass to be able to hear in both ears , but people who can not try in one ear can still often see the generator of speech sound . This is because the brain can use the sound ’s reflection off of the Earth’s surface in one ear to try out to focalize the strait ’s root .
When a healthy wave reaches a somebody ’s eubstance , it reflects off of the person ’s head and shoulder . It also reflects off of the curved surface of the person ’s outer capitulum . Each of these reflections pull in elusive change to the sound wave . The reflecting waves interfere with one another , causing parts of the waving to get bigger or smaller , changing the auditory sensation ’s bulk or timber . These change are known ashead - related carry-over functions ( HRTFs).Unlike with ILDs and ITDs , the phone ’s pinnacle , or the slant at which it hits your ears from above or below , affects its reflections of the surfaces of the body . The reflections are also dissimilar reckon on whether the sound comes from in front of or behind your consistence .
HRTFs have a elusive but complex effect on the shape of the wave . The mind interprets these remainder in the wave ’s contour , using them to find the sound ’s origin . We ’ll calculate at how researchers have study this phenomenon and used it to produce virtual surround - phone systems in the next plane section .
Studying Sound Reflections
The auricle of a somebody ’s pinna has fortune of surfaces that can reflect sound waves . Most of these surfaces are arch . Some might direct the strait toward other surfaces in the ear , induce the wave to ricochet more than once before get through the tympanic tissue layer . Interactions with a person ’s expression , head , hair and torso are complicated as well . Attempting to isolate and quantify each of these reflexion by hand would be almost unimaginable . For this intellect , scientists have studied psyche - related conveyance functions ( HRTFs ) using sound sources , lots of microphone and computer programme .
In some cases , research worker have attached tiny microphone to the surfaces of human participants ' body . In others , they have used pictorial mannequins design to accurately represent a person ’s skin , cartilage and trunk proportions . One such mannequin is the Knowles Electronic Manikin for Acoustic Research , or KEMAR , which has been used in HRTF research in laboratories such as the MIT Media Lab .
These microphones have one business - to enchant sound . Computers can then analyze subtle differences in sounds with unlike points of origin or in the path a undivided sound interacts with different parts of the eubstance . Eventually , this information conduct to analgorithmor coiffe of algorithmic program . The algorithm is basically a mathematical group of rule that describes the elbow room the HRTFs and other ingredient change the conformation of the sound waving . apply the algorithm to another sound undulation change its shape as well , give it the same property that the first wave had after it interacted with the person ’s consistence .
algorithm like these are at the heart of practical environs - speech sound systems . Here ’s what go on :
In other quarrel , the cognitive operation apply aural clue to the audio wave , fooling your brain into understand the sound as though it came from five generator instead of two .
Virtual Surround Sound Tools and Techniques
In plus to sound waves ' interaction with the human body , practical surroundings - sound speakers use a number of tools and techniques to make the illusion of 5.1 - line phone . Some systems , specially digital sound - processing systems , physically reflect profound moving ridge off of the walls of the room . In this case , some of the sound seems to amount from behind you because it is bouncing off of the wall behind your head . Systems like these often necessitate you to allow for the dimensions of your room or to calibrate the speakers using a microphone . Otherwise , the reflections may happen at the wrong angle or in the wrong places .
Many two - verbalizer systems also incorporatecrosstalk cancellation . This is fundamentally the creative usance ofdestructive interferenceto rule out unwanted hindrance between the sound you should hear with your left ear and the audio you should hear with your right . This make it less probable that your spike will plunk up on one another ’s discriminative stimulus , ruining the illusion of five - loudspeaker system sound .
The algorithm and crosstalk cancellation protocols need the help of a computer processor , ordinarily found in a pass catcher / amplifier . This gimmick include a wakeless - action chip that can apply the algorithmic program to the sound waves in actual clock time . As with other amplifiers , it receives the sound information from a source , like a satellite box or a videodisc participant . It applies the algorithmic rule and stool any other adjustment to volume or sound quality before sending the signal to the speakers . In some systems , this receiver / amplifier is build in to the speaker units .
The biggest drawback to practical surround - sound systems is that their immersive outcome is an conjuration rather than the intersection of multiple speakers . Maintaining this illusion command you to sit in the right point and to bet directly at the television screen . Moving too far to the left or the right of thesweet spotcan interrupt the sense impression of real surround sound , place you outside of the directed sound field . Sometimes , sounds that move from one side of the room to the other or from in front of you to behind you seem to be interrupted or voice affected . Since the sound wave themselves are only coming from two speaker , the well-grounded field of operations often has less ability and impact than one from a full curing of speakers .
In addition , there are a few points to keep in intellect if you are shopping for a practical surround - sound system :
To read more about virtual environment sound and related matter , check out the liaison on the next Sir Frederick Handley Page .
Lots More Information
Related HowStuffWorks Articles
More Great Links
Sources