Have you ever wondered what die on inside an electric motor ? We ’ve taken apart a simple electric motor that you would typically retrieve in a toy to explicate how all the parts act upon . See the next Sir Frederick Handley Page to get started .
From the exterior , you could see the steel can that forms the body of the motor , an axle , a nylon end pileus and two battery leads .
The nylon end cap is held in situation by two tabs that are part of the steel can . By bending the tabs back , you could free the destruction pileus and remove it .
Inside the conclusion cap are the motor ’s brush . These brushes transfer ability from the battery to the commutator as the motor spins .
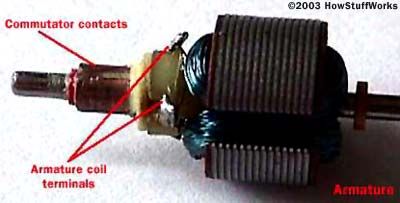
The axle holds the armature and the commutator . The armature is a circle of electromagnets , in this case three . The armature in this motor is a curing of sparse alloy plate stacked together , with thin cop telegram coiled around each of the three poles of the armature .
The two ends of each conducting wire ( one conducting wire for each celestial pole ) are solder onto a terminus , and then each of the three terminals is wired to one plate of the commutator .
The final piece of any DC galvanizing motor is the field magnet . The field attractive feature in this motor is formed by the can itself plus two curved lasting magnets .
One end of each attractive feature rests against a slot cut into the can , and then the retain clip presses against the other ends of both magnets . To learn more , seeHow Electric Motors Workor test your noesis with theElectric Motor Quiz .