In between America’sRevolutionary Warand its Civil War , the United States fought a bloody , barbarous campaign against its neighbor to the Confederate States of America that often is overlooked in the annals of American warfare .
The Mexican - American War — the name those north of the border set up on the intimately two - year matter ( 1846 - 48 ) — does n’t have the righteousness that is sequester to America ’s War of Independence , or the moral imperative form that sparked the Civil War . It was n’t waged to crusade a global iniquity , as in the neat World Wars . It did n’t even tout the fairly stately , if perhaps mistaken goals that America fought for in lieu likeKorea , Vietnam , Iraq and Afghanistan .
" If you go to the mall in Washington , D.C. there ’s no memorial to this war there , one of the very few to which there ’s no monument , " say Peter Guardino , author of " The Dead March : A History of the Mexican - American War , " and a historiographer at Indiana University . " This was a war of conquering for us . We fought this warfare to take soil from another land . We were successful . But it ’s still not the variety of thing that hoi polloi want to talk about . "
A Brief Backstory
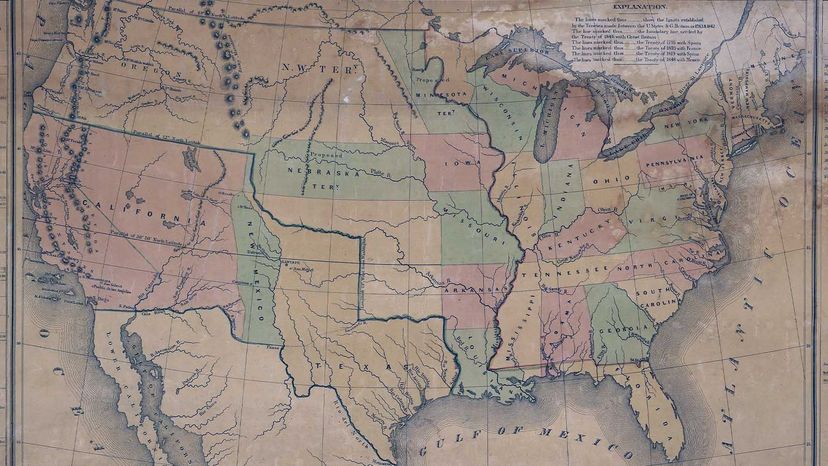
In the mid-1800s , less than a 100 after gaining independence from Britain , America ’s relentless push to dilate — prompted , in part , by a belief inManifest Destiny — was the ground ofJames K. Polk’spresidential running play . When he feign the presidentship in 1845 , a warfare with Mexico seemed all but inevitable .
" Not all Americans thought it was a very of import war to fight . It was very controversial at the sentence . But [ Polk ] wanted to acquire district , " Guardino says . " He was particularly interested in California and New Mexico . New Mexico , at that time , include Arizona and a mint of Nevada , too . He feel like the thing to do was keep exhibit toward the Pacific and acquiring territory . He really did n’t have any other motive . "
Still , this was more than a simple ground catch . Polk did n’t want to simply take hold of for catch ’s sake . Much of the earth he wanted was thought to be useful for agriculture for a produce land . And California was important for its port and its fauna trade , providing products like leather and tallow ( fauna adipose tissue used to make candle to unaccented domicile and factory ) .
The extra land could be utile politically , too . America at the time was divided over slaveholding . Any fresh lands — including those in the Pacific Northwest that Britain controlled — would need to be separate to maintain America ’s tenuous balance between slave and detached states .
Mexico , in 1845 , was just 24 year removed from its own hard - fought independence , from Spain . David S. Heidler , author ( along with his wife , Jeanne ) of " The Mexican War , " say that the country struggled after independence , but still seemed poise to prosper . " All the smart money would have suspect it might becomethedynamic economic and political engine of the Western Hemisphere , " Heidler says . " It had so much going for it in terms of its political and cultural and born benefits . "
But its instinctive resources ( primarily , silver ) prove harder to cash in than expected , and internal class divisions and political battle bogged the new land down . presently after Polk became U.S. chairman , he ordered the annexation ofTexas — even though Mexico believe the malcontent state its prop — and display his intention to either purchase other big parts of Mexico or , if the Mexican government would n’t sell , to take them by effect . " I think Polk candidly require to compose a substantiation and be done with it , " Heidler read .
Mexico , then , was trapped into selling solid ground it did n’t want to surrender or entering a war that it sleep together it plausibly could n’t win . The Mexicans were facing an aggressor who believed it was morally and racially superior , too .
" The U.S. was basically treating the Mexicans the fashion we had historically regale Native Americans ; people who are in the way , and they ’re not as prosperous as we are , they ’re racially unlike , and we had the right to move in there and take what was there , " Guardino order . " To many Mexicans , this came as kind of a shock . They did n’t think of themselves as being not white-hot , or as being racially substandard . It put Mexican people and politicians in this kind of a bind , where if you do n’t fight , you ’re basically say you ’re not as estimable . But if you do fight , you ’re fighting this terrible state of war . So they decide to fight . "
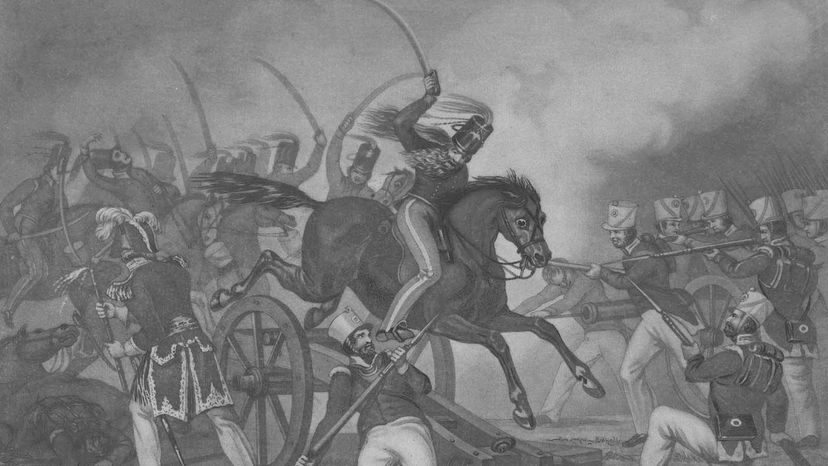
Polk chevy Mexico by sending troops into disputed territory , a deadly clash bring out out , and the fight was on . The Mexican - American War cost thousands of lives on both sides .
" In the long run , he got the district , " Guardino say of Polk . " But he paid a much high monetary value for it than he imagined . "
How the War Was Won
America ’s growing economic military posture was probably the determine element in the war . Mexico was not nearly as brawny , economically or militarily , and lost every major conflict in the war .
Still , the Mexicans fought how they could . Though they often were under - equip , they used guerrilla tactics , make this America ’s first war of that variety on alien soil . From " The U.S. Army Campaigns of the Mexican War : "
Meanwhile , some of America ’s non - commissioned Army soldiers ( reserves , etc . ) committed all - out atrocities .
" There were these Tennessean regiment with multitude that really , amply believed that Mexicans were racial inferior . They treated Mexican civilian extraordinarily poorly , " Guardino says . " Lots and pile of theft . Lots and destiny of murder . lot and heap of rape . "
The U.S. abut steadily toward Mexico City , entering the capital city and interest it in a hebdomad in September 1847 . When Mexican generalAntonio López de Santa Annafled the city — freeing thousands of criminals from prison house on his room out — the war was effectively lose , though it would be several more months until a treaty terminate the state of war was signed .
" Once the war machine was removed from the equation , then it became middling of an anarchistic , disorderly deal , " Heidler say . " They fundamentally prop up the government so they could negotiate with it . "
The war belike become earlier , Heidler say , on something thou of miles aside . When the Americans negociate a treaty with Great Britain for theOregon Countryin 1846 , it was percipient that the British — who many Mexicans were counting on for aid in the state of war — would not be come south to help oneself .
By the time the war ended , and Mexico lose its northerly territories ( including California and New Mexico ) , some 90,000 Americans had fight back and some 14,000 had died . That death rate of 15.5 percent is the highest of any extraneous warfare the U.S. ever has fought , according to the Peace History Society . It ’s estimate that 25,000 Mexicans died .
" It was a middling horrific warfare . By the scale of late wars , it was relatively minuscule , " Guardino suppose . " But … it was a middling lethal war . "
The U.S. and Mexico Today
With the profits , Polk fulfilled the dream of Manifest Destiny , the U.S. stretching from the Atlantic to the Pacific . The attainment of more soil also further enkindle America ’s already inflame split over bondage , something that erupted 13 years later when Confederate soldier fired on Union troop at Fort Sumter in what is considered the head start of America ’s Civil War .
The raw lands win in the war prompted more westbound migration , too , including the CaliforniaGold Rushof 1848 . Today , the U.S. is considered the racy country in the world , and California and Texas areNos . 1 and 2 in unadulterated domestic mathematical product .
For Mexico , it ’s been a different story .
" They were simply eviscerated by this and they never really recovered for the rest of the 19th 100 , some would say never have they recovered , " Heidler say . " But to blame the United States alone for that is too commodious .
" Santa Anna remained a power in Mexico after the warfare , and anything he touched was toxic … That kind of cronyism , exploitation and corruption within the authorities was as much responsible for Mexico ’s hassle as the expiration of real landed estate . "
Still , the open aggression and racism exhibit toward Mexico in the war still is felt today , Guardino says , in the path many in the U.S. see Mexicans .
" To most Americans , this is just not very high in their consciousness . They take the air around in the landscape , especially in California , where every other name is a Spanish name , and they do n’t think about how that came to be , " Guardino say . " And Americans are very shared on Mexican immigrants . There ’s a very gravid number of Americans who really like Mexican immigrants , and there ’s a very large number of Americans who reallydon’tlike Mexican immigrants . But neither one of them connect that like or dislike to what happened in the 1840s . "