Key Takeaways
Sometimes we talk about theConstitution of the United States — the papers that lays out the natural law of the land for Americans — as if it were forged by gods on Mount Olympus and drifted down from the vault of heaven , full formed intoGeorge Washington ’s own mitt , a flawless and sublime document .
The truth about the making of the Constitution is that it was a full mess — like , a " Real Housewives"-franchise - degree mess . It took an unbelievable amount of cloggy lifting to get it into working purchase order , and since it became the supreme law of the state in 1789 , it ’s beenamended 27 time , with one amendment ( the 21st)repealinga previous amendment ( the 18th ) . And we ’re still squabble over whether an 18th - 100 document can meet the motive of 21st - century mass . But blemished as it may be , the Constitution is pretty telling , considering its creation was need to fix the major failing of its predecessor , theArticles of Confederation .
A Terrible First Stab at Government
" The United States ' first constitution , the Articles of Confederation , was fatally flawed from the moment it was adopted , " saysStephen Phillips , a professor of political science at Clemson University . " It make a national government with very little power that was fundamentally impossible to exchange , and that consist of only a general assembly — no sovereign executive or judiciary . "
The government typeset up under the Articles of Confederation was so bad it only endure a decade . And it was n’t so much a government as a " unwavering league of friendship " between the 13 original states , which could all vote on issue that affected the collective , but decisions were only made when at least nine of the states voted the same way . It was a dicey time in American story .
" economical and security crises mounted throughout the 1780s , showing the national government was simply ineffectual to represent to protect the internal stake , " says Phillips . " Political leaders recognise that the country need a strong national political science , which mean a revised make-up . Amid the desktop of political crisis , the Confederation Congress pass a rule of delegates from the United States Department of State to deliberate amendments to the Articles of Confederation to make a stronger internal regime with keen power . The important question for the delegates is what this government would look like and what world power would it have . "
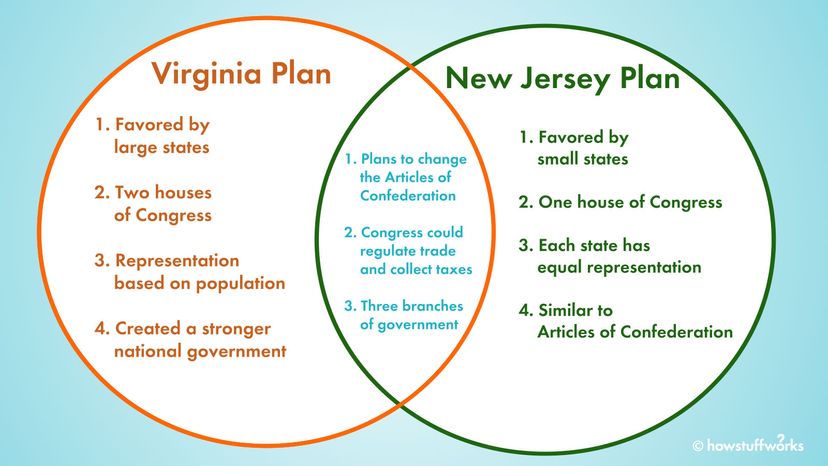
The Virginia (Large-State) Plan
put down the Constitutional Convention of 1787 , wherein 55 delegates from each state met in Philadelphia to address the problems with the Articles but ended up entirely overhauling the U.S. government instead .
It get with James Madison , a phallus of the Virginia House of Delegates , introducing the Virginia Plan , which purpose a much more sinewy interior government withthree branches : a legislative body , administrator and judiciary .
" A key part of the Virginia Plan was a legislature with two dissimilar chambers , a lower house and upper theater where the number of representatives each state had would be determined by its population or wealth — the large the universe , the greater the delegacy it would have , " says Phillips .
The key components of the Virginia Plan :
The New Jersey (Small-State) Plan
Of of course , state with smaller populations were not keen on the idea of a general assembly where representation in both houses would be establish on population , as it would jeopardize their independence and king . In response to the Virginia Plan , the humble states pop the question the New Jersey Plan . The New Jersey Plan , written mainly byWilliam Paterson , voted to keep the single - mansion legislature with equal state representation from the Articles of Confederation , while adding a national executive and a judicatory , and expanding the power of the internal government .
The key factor of the New Jersey Plan :
Large States vs. Small States
In this means , the Constitutional Convention of 1787 become into a grudge match between the orotund states and the small Department of State . After a few days of debate , the New Jersey Plan was reject — even a few people who helped Paterson write the plan vote against it . But the minor states were so dysphoric with the unsuccessful person of the New Jersey Plan and the legislature bid by the Virginia Plan that there was a real theory they would go forth the Constitutional Convention .
At this point , it became light that a compromise on histrionics was necessitate between the large and diminished states . After much debate , delegates correspond to the Connecticut Compromise , insert by Connecticut ’s Roger Sherman and Oliver Ellsworth .
" The Connecticut Compromise proposed a national legislature wherein the lower house internal representation would be based on universe and the upper home states would have an equal vote . The Connecticut Compromise struck a middle flat coat that was capable to win reenforcement from both large and small country , " says Phillips .
The Constitution Evolves
However , the Virginia Plan remained influential at the Constitutional Convention and beyond and is still moot the blueprint for the Constitution . But James Madison did n’t indite the Constitution alone . The main part of his Virginia Plan were take on : a much stronger internal government with the power to tax and provide for the national defense , and a legislative body with two houses , a national executive and a judiciary that share power . After the Connecticut Compromise , there was much argumentation at the Constitutional Convention surrounding what these item-by-item parts would reckon like . There was a spate to forge out around how we would elect the president , the independence of the judiciary , land ' right and representation in the legislative assembly , and a lot of lesser - roll in the hay delegate won on some vital issues .
" There ’s a rationality why adequate State Department representation in the Senate — an idea Madison crusade for tooth and nail — became not only the conventionality ’s greatest via media but now the only permanent , unamendable part of the Constitution , " says Phillips . " The Constitution was written through collaboration and via media . No delegate achieved everything they need , but that did not hold back them from work firmly to make a more utter sexual union . "