To realize the reason for a 1 - bit Dual five hundred / A convertor , it is helpful to know a small about the digital - to - parallel conversion process . In aCD(and any other digital recording technology ) , the goal is to create a recording with very highfidelity(very gamey similarity between the original signal and the reproduced signal ) and perfectreproduction(the transcription sounds the same every clip you play it no matter how many time you act it ) . To action these two end , digital recording converts the analogue waving into a flow of numbers and record the number rather of the wafture . The transition is done by a equipment called ananalog - to - digital converter(ADC ) . Then , to play back the music , the stream of numbers is converted back to an analogue wave by adigital - to - analog converter(DAC ) . The analog wave bring on by the DAC is amplified and run to thespeakersto produce the sound .
When you taste the wave with an analog - to - digital converter you have control over 2 variable :
In the next material body , let ’s assume that the sampling pace is 1,000 per second and the sampling preciseness is 10 :
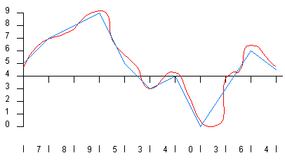
The green rectangles represent samples . Every 1/1000th of a second , the ADC looks at the wave and picks the closest number between zero and 9 . The figure chosen is indicate along the bottom of the figure above . These act are a digital theatrical performance of the original wave . When the DAC renovate the wave from these figure , you get the blue line evidence in the following chassis :
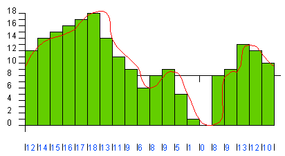
you may see that the blue melody lose quite a minute of the detail primitively found in the red transmission line , which mean the fidelity of the reproduce undulation is not very good . This is thesampling error . You come down sampling erroneous belief by increase both the sampling rate and the precision . In the next image , both the charge per unit and the precision have been ameliorate by a factor of 2 ( 20 gradations at a pace of 2,000 samples per secondly ):
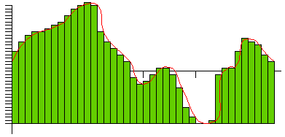
In the next material body , the pace and the precision have been replicate again ( 40 gradation at 4,000 samples per second ):
you could see that as the pace and precision improve , the faithfulness ( law of similarity between the original wave and the DAC ’s yield ) improves . In the case of CD sound , faithfulness is an of import goal , so the try out rate is 44,100 samples per second ( 44.1 KHz ) and the number of gradations is 65,536 . At this level , the yield of the DAC so closely matches the original wave form that the sound is fundamentally " perfect " to most human ears .
The DAC typically utilise a differentresistorfor each bit . A 4 - bit DAC take 4 resistors working in line of latitude to provide a steadfast analog signal . When you get to the 16 - bit or even 32 - bit grade found in CDs andDVDs , the numeral of gradation required per resistance get it very hard to precisely match value . For example , a distinctive 16 - bit DAC would have 16 resistors require a total of 65,536 gradations .
What a1 - bit Dual D / A converterdoes is allow the digital - to - analog conversion to happen without the need for all those surplus resistance . fundamentally , this type of DAC does not expend a bank of resistors operating in parallel . alternatively , it creates a carefully modulated signal from the digital . The converter relies onnoise shaping , a phenomenon that takes reward of the human spike ’s inability to acknowledge interference when it go on in higher frequencies . Basically , the human ear is most sensitive to make noise at 5 KHz , and is almost unable to detect it at 20 KHz .
A key part of the converter is a circuit called adelta - sigma modulator , which takes the binary signal ( 1s and 0s ) from the CD and deepen them to a unfaltering beat , call apulse train . The heart rate train contains an average of the change in the amount of energy represent in the sample distribution . Alow - pass filterremoves all clip - domain entropy and recovers only the average energy of the pulse train that eat it . The keystone here is to understand that the pulse - train waveform is clocked at a very high frequency compared to the 44.1 KHz sampling rate . The pulse power train is transport through the DAC and alter into an analog signal .
The delta - sigma circuit has two primary section :
The error signaling is used by the low - pass filter toaveragethe parallel sign . essentially , this signify that moment adaption are made to the parallel signal to compensate for the differences between the binary sign and the pulsation caravan . This pageprovides unbelievable detail and diagram of the entire circuit , as well as a detailed explanation of the process .
Here are some interesting links :